Fig. 1. Activity of the depalmitoylating enzyme APT1 is required for asymmetric localization of Numb and β-catenin.
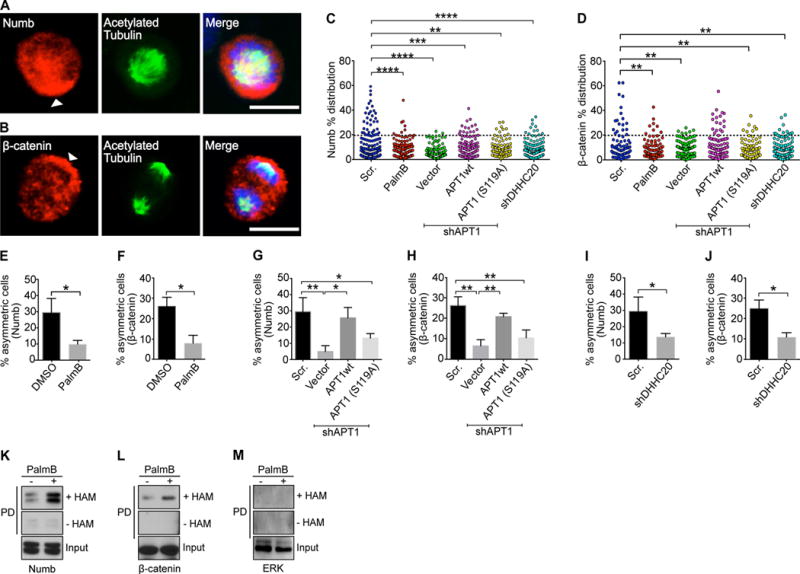
(A and B) Images of dividing MDA-MB-231 cells stained to show endogenous Numb (A) and β-catenin (B) in red, acetylated tubulin in green, and nuclei in blue. Arrowheads indicate asymmetric localization of Numb and β-catenin. Scale bars, 15 μm. (C and D) Distribution dot plots showing the difference in mean fluorescence pixel intensity of endogenous Numb (C) and β-catenin (D) across dividing MDA-MB-231 cells. The distribution of the percentage differences of all quantified cells was plotted, and cells with a difference of >20% (black dotted line) were scored as asymmetric. n= 508-582 cells scored for each experimental group. Each dot represents a single cell. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the indicated groups. (E and F) Quantification of dividing MDA-MB-231 cells showing asymmetric Numb (E) and β-catenin (F) localization after treatment with PalmB or DMSO. (G and H) Quantification of the number of dividing MDA-MB-231cells showing asymmetric Numb (G) and β-catenin (H) localization when APT1 was knocked down with shAPT1, and when wild-type APT1 (APT1WT) or the catalytically inactive APT1S119A mutant was coexpressed with shAPT1. Cells expressing a scrambled (Scr) shRNA sequence were used as a negative control for APT1 knockdown, and cells expressing the empty vector were used as the negative control for the APT1 rescue experiments. (I and J) Quantification of the number of dividing MDA-MB-231 cells showing asymmetric Numb (I) and β-catenin (J) localization when DHHC20 was knocked down with shDHHC20. (K to M) Immunoblots showing biotin-labeled Numb (K), β-catenin (L), and Erk (M) in MDA-MB-231 cell lysates following acyl-biotin exchange (ABE) assays and pulldown on streptavidin beads (PD). Cells were grown in either in the presence either PalmB or vehicle control (DMSO). Input lanes show cell lysates prior to pulldown. Samples without hydroxylamine (-HAM) were negative controls for the ABE reactions. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 T-test (E and F) or ANOVA (G to J). Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD).
