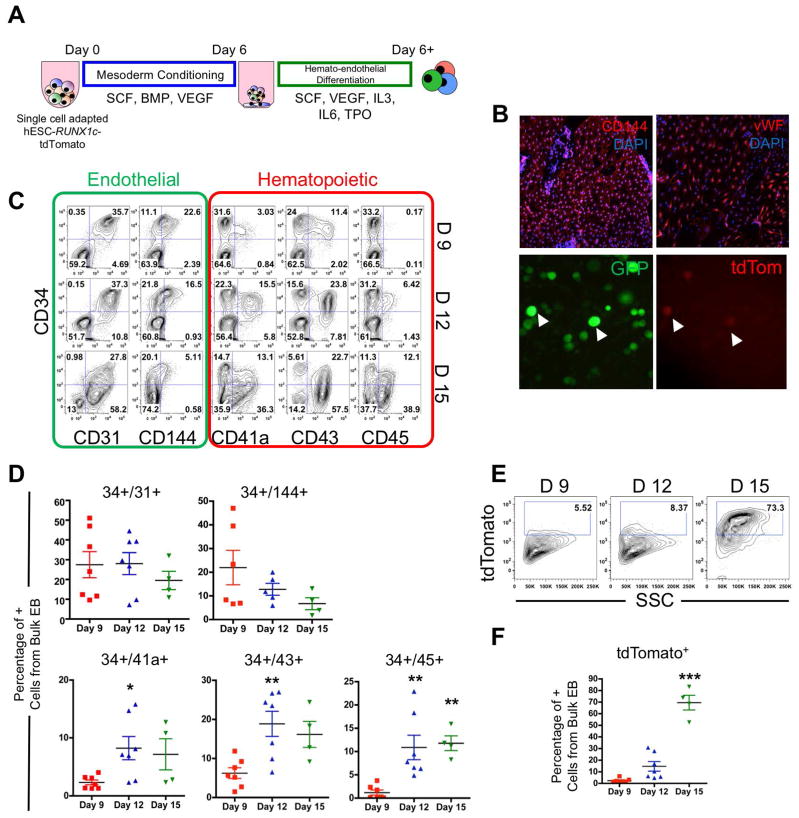
Figure 1. hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato cells can model the human endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition (EHT) in vitro.
(A) Schema of hemato-endothelial differentiation from hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato cells as spin embryoid bodies (spin-EB). (B) Top; Representative immunofluorescent images of hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato at Day 9 of differentiation for endothelial specific surface antigens CD144 and vWF (red). Original magnification is 40x. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Representative immunofluorescent images of hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato at Day 12 of differentiation demonstrating development of non-adherent, dual constitutive GFP+ (green) and tdTomato+ (red) reporter hematopoietic cells from spin-EBs (bottom panels). Magnification 200x. (C) Representative flow cytometry plots of endothelial (CD31, CD144) and early hematopoietic surface antigens (CD41a, CD43, CD45) at Day 9 (D9), Day 12 (D12) and Day 15 (D 15) time points over the course of hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato differentiation. (D) Quantification of flow cytometry as shown in panel C. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 as compared to Day 9 assessed by one-way ANOVA + Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test. Each data point represents a distinct hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato differentiation and errors bars represent SEM; n=4–7 (E) Representative flow cytometry plots of tdTomato (RUNX1c) expression at Day 9 (D9), Day 12 (D12) and Day 15 (D 15) time points over the course of hESC-RUNX1c-tdTomato differentiation. (F) Quantification of flow cytometry as shown in panel E. ***p<0.001 as compared to Day 9 assessed by one-way ANOVA + Tukey-Kramer post-hoc test, error bars represent SEM; n=4–7 independent, biological replicates.