Figure 1.
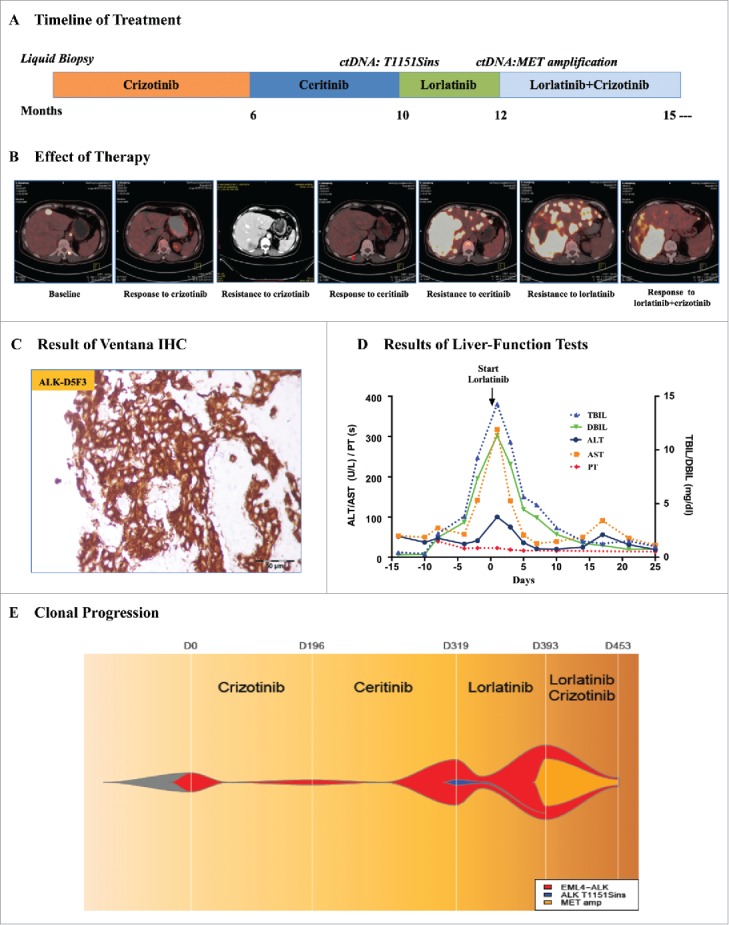
Plasma ctDNA revealing the resistance mechanism of ALK inhibitors. A. The multiple treatments the patient received for metastatic anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive lung adenocarcinoma and the duration of each treatment. B. Computed tomography (CT) or positron emission tomography (PET)-CT images of the patient's metastatic liver lesions chronicling the response to treatment with various ALK inhibitors. C. Ventana (D5F3) ALK Immunohistochemical (IHC) assay analysis of the left lung biopsy tissue. D. Serial monitoring of liver-function before and after treatment with lorlatinib. E. Clonal evolution of resistance to ALK inhibitors in the patient. This model was according to captured-based ultra deep sequencing analysis of pretreatment and resistant plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). TBIL, total bilirubin; DBIL, direct bilirubin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, Aspertate Aminotransferase; PT, prothrombin time.
