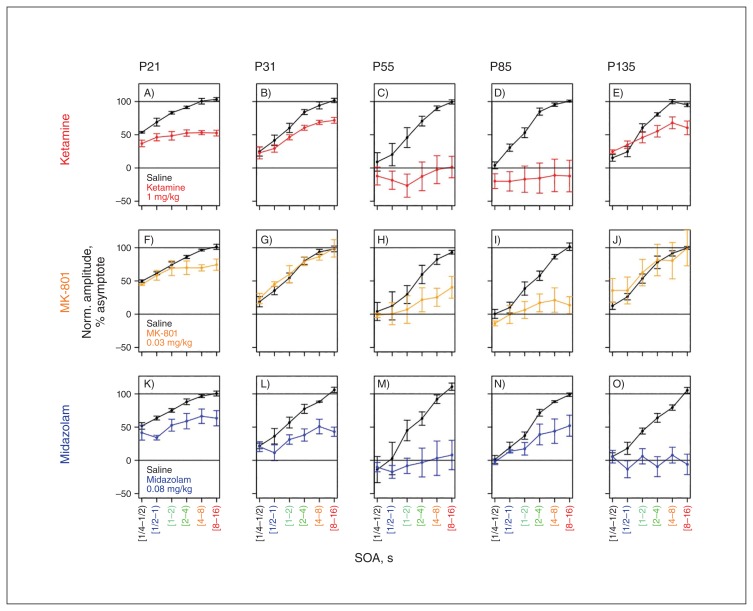
Fig. 4.
Effect of ketamine, MK-801 and midazolam on refractoriness. Individual panels show normalized component amplitude as a function of stimulus-onset asynchrony (SOA) averaged across all 4 animals for vehicle sessions (black) and drug trials (colour code). Error bars represent standard error of the mean across animals. At larger SOAs, component amplitude saturates, typically between 8 and 12 seconds. (A–E) Ketamine: blunted scaling of amplitude with SOA is apparent across all components. The effect of ketamine is most pronounced on components P55 and N85. Scaling of amplitude with SOA is more resilient to ketamine for components P31 and P135. (F–J) MK-801: blunted scaling is apparent for the P55 and N85 components. The effect of MK-801 is limited for P21 and seems completely absent for P31 and P135. (K–O) Midazolam: blunted scaling of amplitude with SOA is apparent across all components. In contrast to ketamine, N85 retains amplitude scaling, whereas P135 does not.