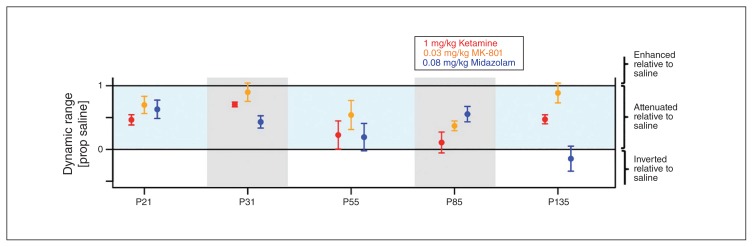
Fig. 7.
Different response profiles of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) blockers and γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) positive allosteric modulator (PAM) midazolam. Normalized dynamic range on the Y axis is plotted for all 5 components and all 3 psychoactive agents. A value of 1 indicates no change in dynamic range. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the mean. Ketamine (red) causes widespread attenuation, which is greatest in the later components (P55, N85) and more subtle in the earlier components (P21 and P31). MK-801 (orange) has a similar profile to ketamine, but overall causes less attenuation for all components. Midazolam (blue) exhibits a different profile of attenuation with relatively stronger attenuation for P31 and P135 and relatively weaker attenuation for N85.