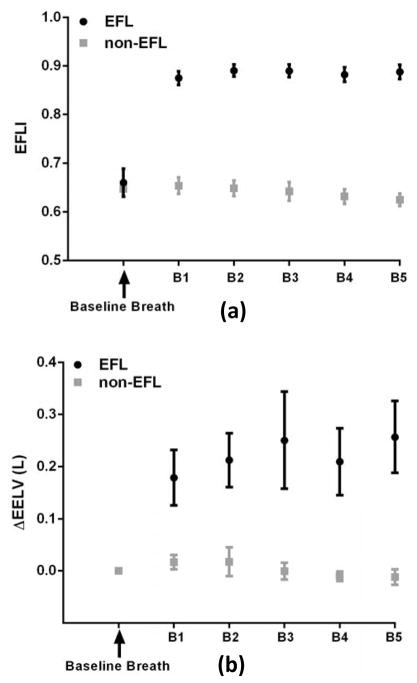
Figure 6.
Expiratory flow limitation index is associated with an increase in end-expiratory lung volume (calibrated thoracoabdominal inductance plethysmography), consistent with increased expiratory resistance and reduced expiratory flow. (a) The EFLI was above 0.8 for all EFL breaths and below 0.7 for all non-EFL breaths. (b) The ΔEELV for expiratory flow limited (EFL) breaths was significantly larger than for non-expiratory flow limited (non-EFL) breaths. EFLI was calculated from pneumotachograph flow. B1 to B5 denote the breath number 1 to 5.