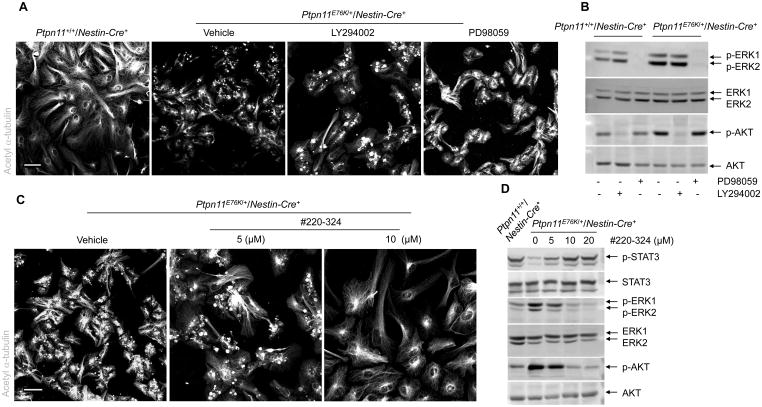
Fig. 6. Inhibition of SHP2, but not ERK or AKT, rescues ependymal cell differentiation of Ptpn11E76K/+ NSPCs.
(A–D) Lateral ventricular walls dissected from newborn pups (n=3 mice per genotype) were processed for ependymal cell differentiation assays in the presence of the MEK1 inhibitor PD98059, the PI3K inhibitor LY294002, the SHP2 inhibitor #220-324, or vehicle. Inhibitor-treated cells were immunostained for acetyl α-tubulin to mark cilia (A, C) and examined by immunoblotting for phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT), phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK), and phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) (B,D). Analyses in all panels were performed in 3 independent experiments. Representative images are shown. Scale bars, 50 μm.