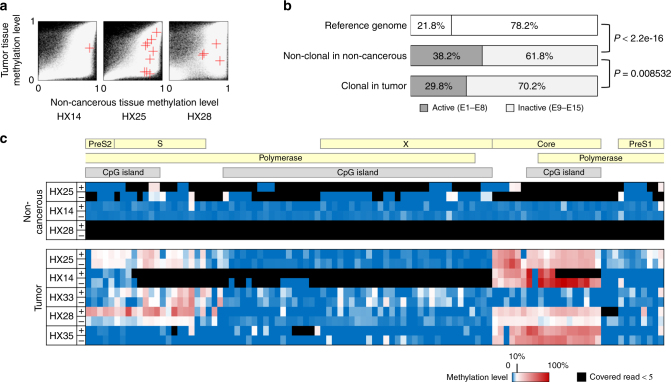
Fig. 5.
Integration and methylation of HBV genomes in hepatocellular carcinoma genomes. a Comparison of the methylation levels of the regions of tumor genomes (y-axis) that included the HBV-integrated sites with the methylation levels of the same region of non-cancerous genomes (x-axis). A red cross indicates the position of a region including the integration of HBV. In the background, a white dot shows a genomic region, and a black indicates no data. b Proportion of the HBV-integrated sites in active or inactive chromatin areas. The integrated sites were detected using whole-exome and oncovirome sequencing. Reference genome: the proportion of the base numbers of chromatin states in the normal adult liver defined in ENCODE;7 non-clonal: the proportion of the numbers of integration sites (tag count ≥2, ≤3) in 108 non-cancerous liver samples; clonal: the number of integration sites (tag count ≥5) in 102 tumor samples. The P value was calculated using Fisher’s test. c The methylation levels of all CpG sites in the HBV genome detected by whole-genome bisulfite sequencing of HCC samples