FIGURE 2.
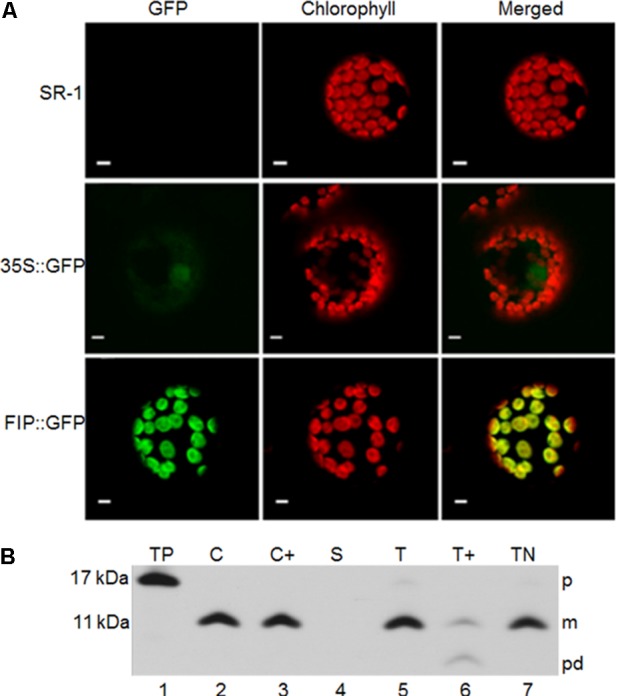
Subcellular localization of FIP. (A) In vivo chloroplast localization of the FIP::GFP fusion introduced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens–mediated transfection in tobacco protoplasts. Fluorescence images were obtained using a confocal laser scanning microscope. green fluorescent protein (GFP) corresponds to the fluorescence detected in the green channel. Chlorophyll, detected in the far-red channel, corresponds to the chloroplast autofluorescence signal. Chlorophyll + GFP corresponds to the merging of the far-red and green channels. Yellow represents the co-localization of green and red signals. All scale bars represent 5 μm. SR-1 corresponds to wild type Nicotiana tabacum non-transformed protoplasts; 35S::GFP corresponds to expression of GFP driven by the constitutive 35S promoter of Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV); FIP::GFP corresponds to expression of FIP::GFP fusion driven by the constitutive 35S promoter of CaMV (B) pFIP is imported into isolated chloroplasts and integrated into thylakoids. Radiolabeled in vitro-translated pFIP (TP, lane 1) was incubated with intact isolated pea chloroplasts in a reaction containing 5 mM ATP and ∼100 μE/m-2 sec-1 light at 25°C for 20 min. Intact chloroplasts were recovered from the reaction (C, lane 2) and treated with thermolysin (C+, lane 3). Untreated intact chloroplasts were fractionated into stroma (S, lane 4) and thylakoids. Thylakoid aliquots were washed with import buffer (T, lane 5), treated with thermolysin (T+, lane 6), or treated with 100 mM NaOH (TN, lane 7). Samples were analyzed by SDS–PAGE on 12.5% gels and by fluorography. The precursor, mature form, and product degradation are designated p, m, and pd, respectively, on the right side of the panels. M-values on the left side were estimated from their migration compared with standard marker proteins.
