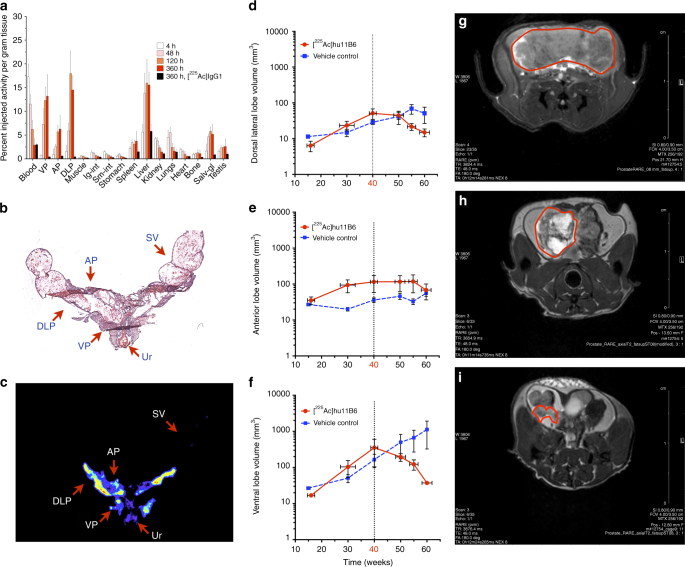
Fig. 3.
Specific and potent therapeutic effect of [225Ac]hu11B6 in the Hi-Myc x pb_KLK2 mouse model that expresses human hK2 in the prostate. a The pharmacokinetic profile of [225Ac]hu11B6 was determined in a biodistribution experiment using genetically modified mice (Hi-Myc x pb_KLK2) with inherent prostate-specific expression of human hK2 and spontaneous development of prostate adenocarcinoma. This biodistribution data set shows increasing accumulation of drug in the ventral prostate (VP), dorsal-lateral prostate (DLP), and anterior prostate (AP) lobes with time (n.b., the VP and DLP exhibit higher expressions of hK2 and showed higher [225Ac]hu11B6 uptake compared to AP tissue). H&E (b) and autoradiography (c) of a tissue section (encompassing all three prostate lobes, urethra and seminal vesicles) from a pb_KLK2 x Hi-Myc injected with [225Ac]hu11B6. Radioactivity is only associated with the prostate lobes and not with seminal vesicles (SV) and radiosensitive bystander urothelium (Ur). In a therapeutic study of [225Ac]hu11B6, disease was monitored by volumetric MRI measurements of the individual lobes of Hi-Myc x pb_KLK2 mice. Mice underwent longitudinal MRI commencing at 15–16 weeks of age and received a single 300 nCi dose of [225Ac]hu11B6 at week 40. Lobe volumes are plotted vs. time following the effect of alpha irradiation on the DLP (d), AP (e), and VP (f) respectively. Vehicle-treated animals served as control for tumor progression. The results show that one injection of [225Ac]hu11B6 significantly decreased tumor burden and inhibited disease progression in this GEM model of locally advanced disease. MR images of a representative animal confirms the significant reduction in tumor volume as shown at baseline (pre-treatment) (g) and at 4 (h) and 8 (i) weeks following a single injection of [225Ac]hu11B6