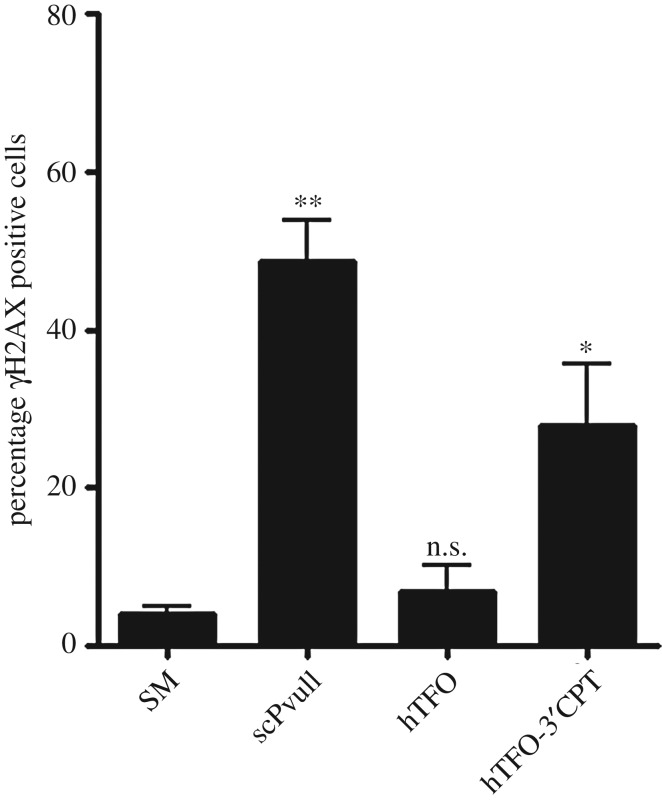
Figure 4.
Induction of DNA damage by TFO-CPT or scPvuII after transfection. A2780 cells were treated with 2 µM of the hTFO-CPT conjugate (and hTFO for control) or 1 µg of scPvuII. After 3 h, cells were collected and stained for phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) and analyzed by FACS. Transfections were performed in duplicate for three independent experiments. Data are represented as means of the means + s.e.m. Statistical comparison was performed between cells treated with Saint Mix only and cells treated with TFO only, hTFO-CPT or scPvuII. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01. The chemical conjugation of the TFO to CPT has been described in detail elsewhere (see Vekhoff et al. [43]. In short, 3′ thiophosphorylated TFOs were conjugated to 10-(6-bromohexyloxy)-CPT and purified by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): hTFO-CPT: retention time 18.6 min; mTFO-CPT: retention time 18.4 min. The conjugates were characterized by UV spectroscopy, denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and mass spectroscopy (ES-MS). ES-MS: hTFO-CPT: found [M-H] 4621.74; calculated: 4621.1. mTFO-CPT: found [M-H] 6988.24; calculated: 6988.8. SM, the delivery agent Saint Mix; scPvuII, single chain PvuII.