Figure 4.
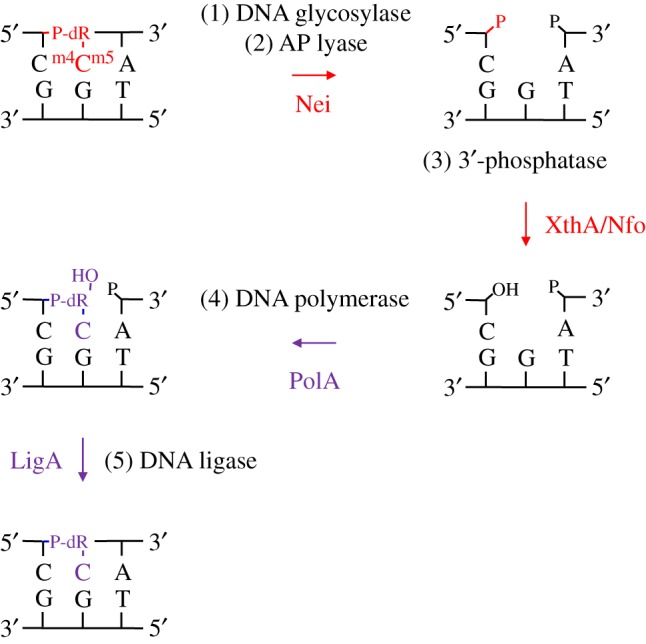
Proposed steps of the E. coli BER pathway for mN4,5C in DNA. Both the damaged base excision step 1 and the AP site incision step 2 are performed by the bi-functional DNA glycosylase Nei as reported here. The 3′-remnant must be removed (step 3) by a phosphatase, which in E. coli may be either a function of XthA or Nfo [35] (figure 2). The cleaned one-nucleotide gap in DNA is now ready for insertion of the correct dCMP (step 4) by the repair DNA polymerase I (PolA) [39] followed by nick-sealing (step 5) by DNA ligase (LigA) [40]. The excised target and newly inserted residues, along with their corresponding reaction arrows, are shown in red and violet, respectively; dR, deoxyribose.
