FIG 4 .
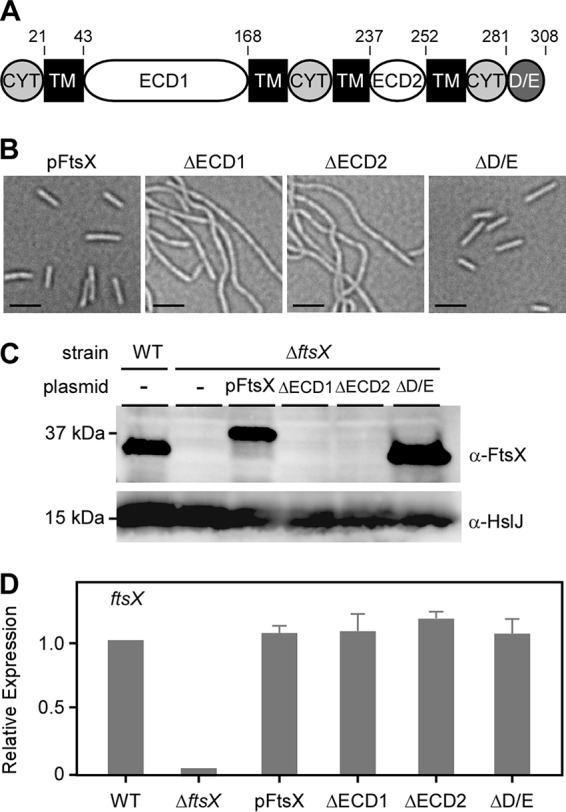
Requirement of the extracellular domains ECD1 and ECD2 for FtsX functionality. (A) Predicted structural domains of FtsX, showing four transmembrane (TM) domains, two extracellular loops (ECD1 and ECD2), three cytoplasmic regions (CYT), and a unique C-terminal aspartic acid/glutamic acid-rich domain (D/E). Positions of amino acids are indicated above the map. (B) Phase-contrast microscopic images of the complementing ftsX strain and its derivatives lacking the ECD1, ECD2, or D/E-rich domain. Bars, 2 μm. (C) Whole-cell lysates of fusobacterial strains grown to mid-log phase and normalized by optical density were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against FtsX (anti-FtsX [α-FtsX]) and HslJ (anti-HslJ [α-HslJ]); the latter serves as a loading control. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left of the blot. Of note, pFtsX contains His and Flag tags. (D) The mRNA expression level of ftsX in indicated strains was determined by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) relative to the parental strain. Values are averages plus standard deviations (error bars) from two independent experiments performed in triplicate.
