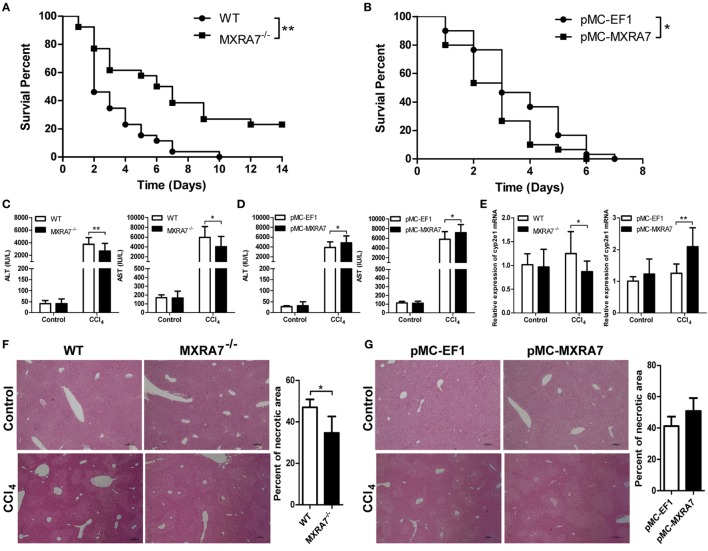
Figure 1.
Matrix remodeling associated 7 (MXRA7) deficiency alleviates, while MXRA7 overexpression aggravates CCl4-induced acute liver injury. (A) Wild-type (WT) and MXRA7−/− mice were administered intraperitoneally with 6 ml/kg CCl4 (1:1 corn oil), and survival of animals were monitored daily for 14 days after n = 26 in each group. The data was expressed as the Kaplan–Meier survival curves and analyzed by the log-rank test. The data shown are the summary of three experiments. (B) C57BL/6 mice were injected with mock pMC-EF1 (control) or pMC-MXRA7 plasmids by hydrodynamic gene transfer method. Three days later, the animals were challenged with CCl4 as above. Survivals were monitored once a day for 7 days after administration. n = 30 each group. The data shown are the summary of four experiments. (C–G) WT and MXRA7−/− mice, or pMC-EF1 and pMC-MXRA7-pulsed mice, were treated with 1 ml/kg CCl4 injection (1:1 corn oil) or control oil. Twenty four hours later, the animals (n = 6 for control group, n = 18–23) were sacrificed and serum were harvested measurement of ALT and AST (C,D), while livers (n = 3 for control group, n = 9 for CCl4) were harvested and subjected to measurement of CYP2E1 mRNAs using reverse transcription-quantitative real-time PCR (E) and structure evaluation after histological hematoxylin and eosin staining (F,G). For histological evaluation, necrotic areas were determined by microscopy. The percentage of necrotic area was determined by dividing the sum area of necrosis by the sum of the total liver area of four fields. One representative section is shown for each group (original magnification: 40×). The data shown are the summary of three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.