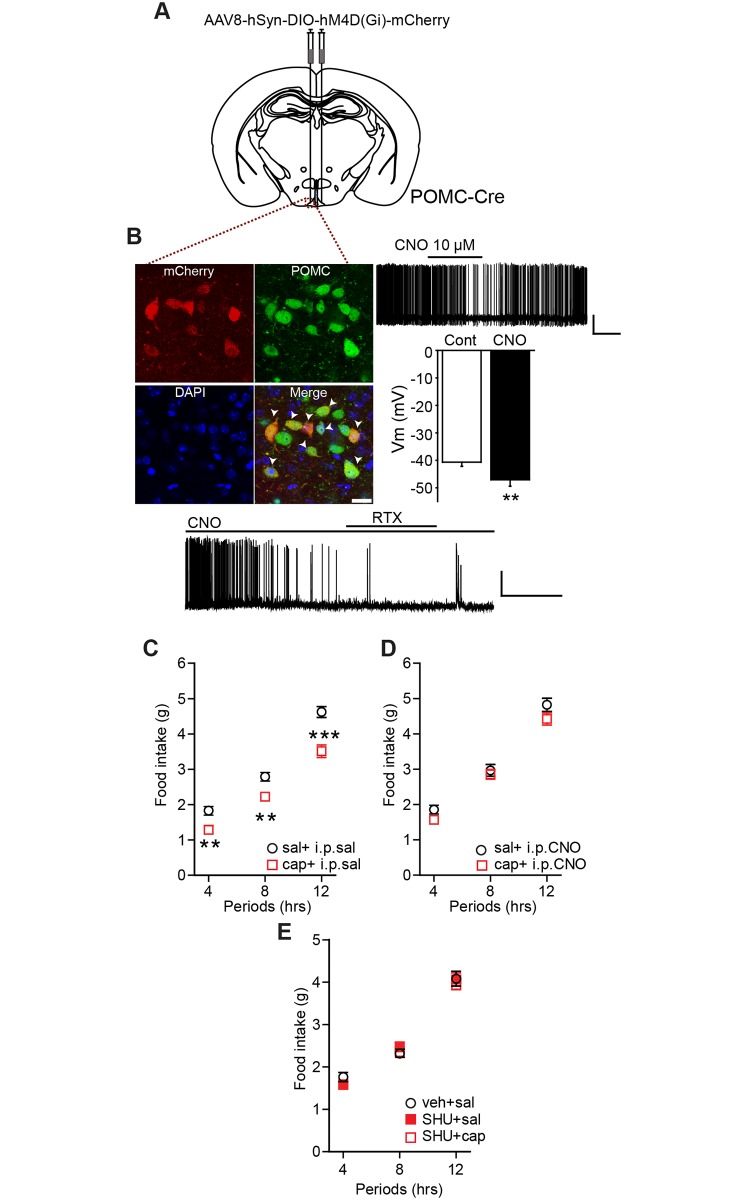
Fig 3. Activation of TRPV1 receptors in ARC POMC neurons reduces food intake.
(A) Schematic drawing of our experimental configuration showing that Cre-inducible AAV-Gi/o-DREADD was injected into the ARC of POMC-Cre mice. (B) Expression of Gi/o-DREADD in POMC neurons in the ARC (top left panel, scale bar: 20 μm). Arrowheads represent POMC neurons that co-expressed mCherry (n = 493 out of 529 mCherry-positive neurons, n = 3 mice). Treatment with CNO (10 μM) hyperpolarized POMC neurons (top right panel; Control, −40.7 ± 1.5 mV; CNO, −47.1 ± 2.3 mV, n = 6 neurons, **p < 0.01). Scale bar: 25 mV, 2 min. Bottom panel: In the presence of CNO, treatment of the TRPV1 agonist was not able to depolarize POMC neurons (n = 3 neurons). Scale bar: 20 mV, 100 s. (C and D) Pooled data from 8 mice showing blockade of the effect of capsaicin by activation of Gi/o-DREADD in ARC POMC neurons. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (E) Pooled data from 11 mice showing blockade of the effect of capsaicin by the MC3/4 receptor antagonist SHU9119 (5 μM). p > 0.05. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. AAV, adeno-associated virus; ARC, arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus; cap, capsaicin; CNO, clozapine-N-oxide; Cre, Cre recombinase; DREADD, designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs; hSyn, human synapsin I promoter; i.p., Intraperitoneal; mCherry, monomeric cherry fluorescent protein; MC3/4, melanocortin 3/4; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; RTX, resiniferatoxin; sal, saline; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptor.