Figure 2. Pulmonary arteries, veins and indeterminate vessels in study groups.
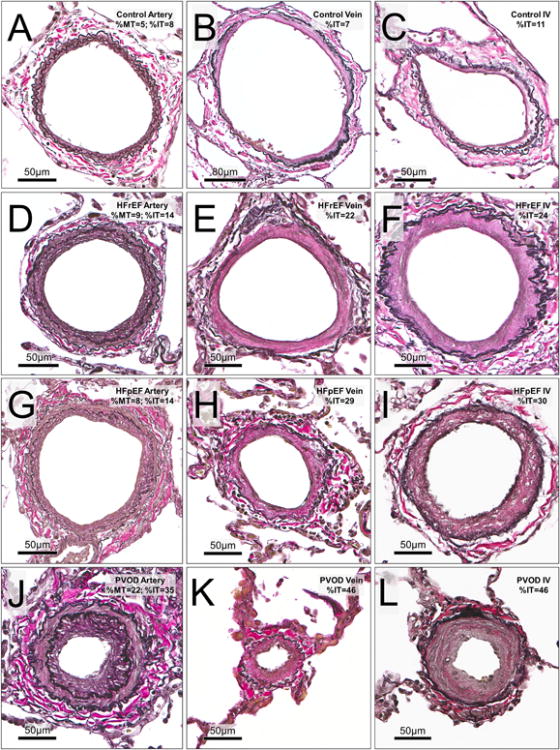
Representative vessels with remodeling approximating the median values for medial and intimal thickening of arteries, veins and indeterminate vessels (IV) in each study group are shown. Rows represent cohort groups (from top; Controls, HFrEF, HFpEF and PVOD). Columns represent vessel type (from left; arteries, veins and indeterminate vessels). In Controls; A (artery:ED152 μm), B (vein: ED 247 μm) and C (IV: ED 121 μm). In HFrEF; D (artery: ED 173 μm), E (vein: ED 181 μm) and F (IV: ED 193 μm). In HFpEF; G (artery: ED 176 μm), H (vein: ED113 μm) and I (IV: ED 175 μm). In PVOD; J (artery: ED 148 μm), K (vein: ED 60 μm) and L (IV; ED135 μm).
Abbreviations: ED, external diameter; HF, Heart failure; HFpEF, HF with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, HF with reduced ejection fraction; %IT, percent intimal thickness; %MT, percent medial thickness; PH, pulmonary hypertension; PVOD, pulmonary veno-occlusive disease.
