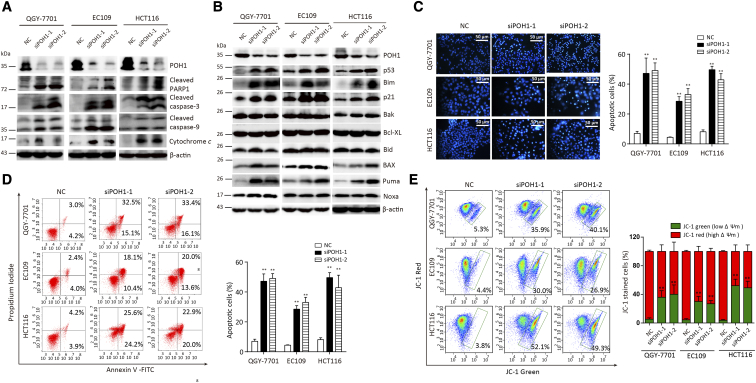
Figure 4.
POH1 knockdown induces cell apoptosis. Cells were treated with POH1 siRNA (siPOH1-1 or siPOH1-2) or scrambled siRNA for 48 hours. (A) Expressions of PARP1, caspase-3, caspase-9, and cytochrome c were examined by Western blot analysis. Cytochrome c was extracted from cell cytoplasm. (B) Expressions of p53, p21, and Bcl-2 family of proteins, including Bak, Bid, Bcl-xl, and Bim, were examined by Western blot analysis. (C) Hoechst 33342 staining of QGY-7701, EC109, and HCT116 cells detected by fluorescent microscopy. Highly condensed or fragmented nuclei represent apoptotic cells. Intact nuclei represent viable cells (×100) (left panel). The percentage of apoptotic cells was recorded (right panel). (D) POH1 silencing induced apoptosis in QGY-7701, EC109, and HCT116 cells. Cells were transfected with POH1 siRNA (siPOH1-1 or siPOH1-2) or scrambled siRNA for 48 hours and then stained with Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) (left panel). The percentage of apoptotic cells was recorded (right panel). (E) POH1 siRNA induced a decrease in the mitochondrial membrane potential. Cells were transfected with POH1 siRNA (siPOH1-1 or siPOH1-2) or scrambled siRNA for 48 hours and stained with JC-1 for 15 minutes. The mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ψm) was determined by FACS (left panel). Graph depicts mean ± SD of three independent experiments (right panel). All *P<.05 and **P<.01.