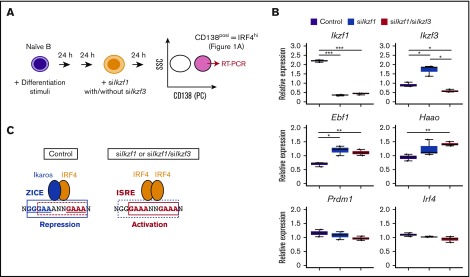
Figure 7.
Loss of Ikaros resulted in upregulation of Ebf1 and Haao genes in CD138posiplasma cells. (A) Schematic representation of knockdown in CD138posi PCs derived by differential stimulation. B1-8hi splenic B cells were stimulated for 48 hours and transfected with knockdown sequences targeting control or Ikaros (siIkzf1) with/without Aiolos (siIkzf3). Cells were cultured for another 24 hours, and CD138posi PCs were sorted and carried for RT-PCR in panel B. As shown in Figure 1A, CD138posi PCs correspond to IRF4hi fraction. (B) RT-PCR of transcripts of indicated genes in control cells and siIkzf1- or siIkzf1/siIkzf3-transfected CD138posi PCs. Ebf1 and Haao, shown as IRF4 target genes possessing ZICE sequences that embed ISRE motifs bound by IRF4 homodimer for gene activation. Prdm1, shown as an IRF4 target gene possessing an ISRE motif. Results are presented relative to the abundance of transcripts encoding Β2m, and shown with box-and-whisker plot. One experiment was performed using 3 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001. (C) Schematic representation of the regulation of ZICE target genes, Ebf1 and Haao, in control and siIkzf1-or siIkzf1/Ikzf3-transfected CD138posi PCs. In control cells, IRF4 effectively binds the ZICE motif as a heterodimer with Ikaros for repressing target gene. In siIkzf1- or siIkzf1/siIkzf3-transfected cells, IRF4 binds the ISRE motif within the ZICEs as a homodimer, resulting in activation of these target genes. ZICE, GGGAANNNGAAA underlined and indicated with blue box; ISRE, GAAANNGAAA indicated with red box.