Figure 1. Two-panel scatterplot depicting 18-month changes in visceral fat by impulsive risk-taking as indexed by the Behavioral Analogue Risk Task (BART) among mothers of children with an autism spectrum disorder (caregivers, high stress) and mothers of neurotypical children (controls, low stress).
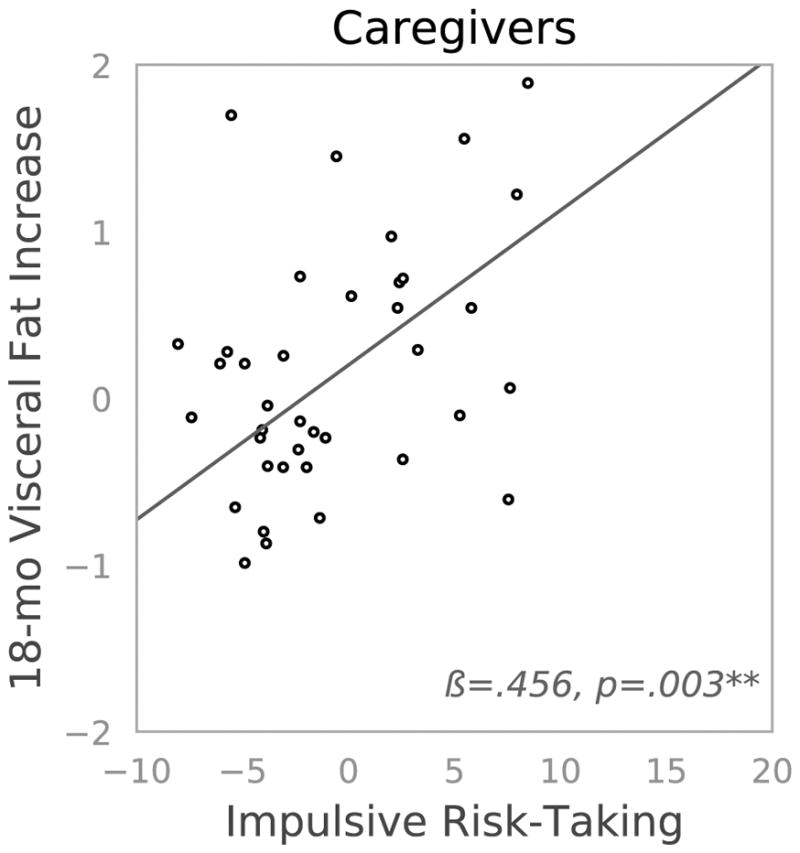

**p ≤.01. Mothers of a child with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD; caregivers) are depicted on the left and mothers of neurotypical children (controls) are depicted on the right. We indexed impulsive risk-taking using the Balloon Analog Risk Task (BART), and mean-centered scores. We quantified 18-month increases in visceral fat as the standardized residualized change score (see data analyses).
