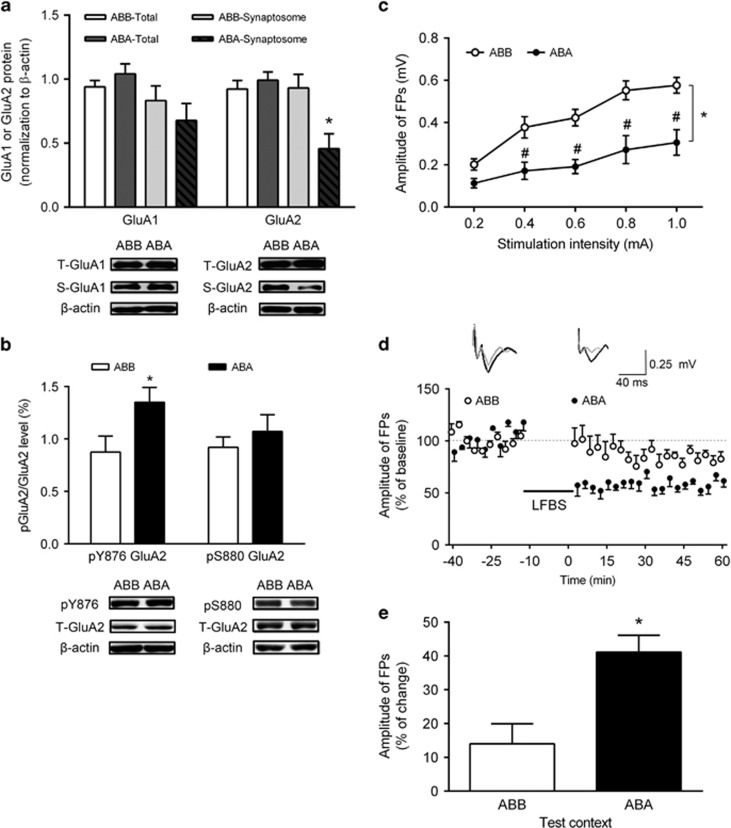
Figure 2.
Re-exposure to heroin-paired context decreased synaptosomal GluA2, increased pY876 GluA2 in the IL, impaired basal synaptic transmission, and facilitated LTD induction in the vCA1-IL pathway. (a) Total and synaptosomal protein levels of GluA1 and GluA2 in IL after context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. *P<0.05 vs the ABB group using unpaired t-test, n=6 per group. (b) Ratio of pY876 GluA2/GluA2 and pS880 GluA2/GluA2 protein levels in the IL after context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. *P<0.05 vs the ABB group using unpaired t-test, n=6–7 per group. (c) Input–output curves. Two-way ANOVA, *P<0.05, vs the ABB group; #P<0.05 vs each stimulation intensity, n=4 per group. (d) LTD induction in the vCA1-IL pathway after LFBS stimulation after exposure to the heroin-paired context, n=4 per group. Representative traces at the baseline and after LFBS stimulation are shown. Calibration: vertical scale bar, 0.25 mV; horizontal scale bar, 40 ms. (e) Summary of the magnitude change of LFBS-induced LTD in each group. Amplitude of FPs after the LFBS stimulation represented as a percent change from the baseline. *P<0.05, vs the ABB group using unpaired t-test, n=4 per group. Data are depicted as the mean±SEM.