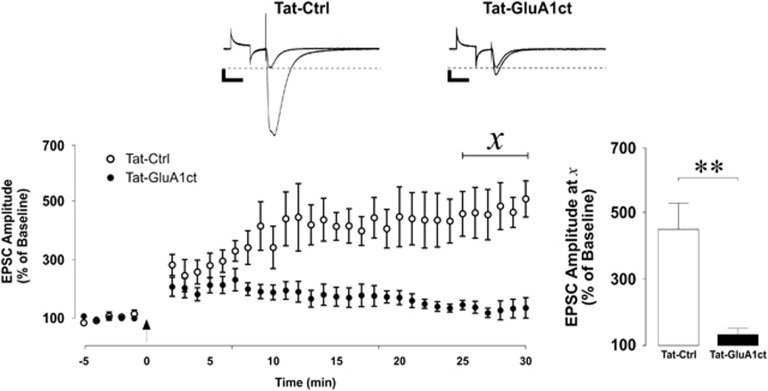
Figure 3.
Synthetic AMPA receptor C-terminal tail decoy peptide inhibits LTP formation in ventral hippocampal CA1 neurons. Long-term potentiation (LTP) of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in the presence of an AMPA receptor C-terminal tail mimic (Tat-GluA1ct) or control (Tat-Ctrl) peptide. Top: representative traces of evoked EPSCs before and 30 mins after LTP induction. Transient response to square-wave command voltage step to monitor input resistance precedes the electrode-elicited AMPA receptor-mediated EPSC. Scale bars represent 100 pA (vertical) and 50 ms (horizontal). Bottom left: scatter plot of mean±SEM amplitude of evoked EPSCs before and 30 mins after LTP induction. Arrow indicates LTP induction (2 Hz, 50 pulses delivered while cell was voltage-clamped at −5 mV). Bottom right: mean+SEM of EPSC amplitude normalized to baseline 30 min after LTP induction. LTP of EPSCs was blocked when recorded in the presence of Tat-GluA1ct. Statistical analysis was performed on the average of values underlying χ reflecting LTP. (Tat-Ctrl: n=5 cells from five rats; Tat-GluA1ct: n=5 cells from five rats) **P< 0.01.