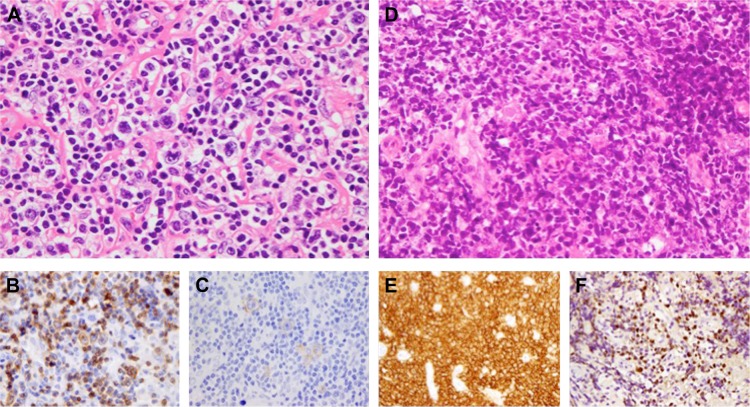
Figure 3.
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) developed during forodesine therapy.
Notes: A 68-year-old female was diagnosed with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Lymph node biopsy at the initial diagnosis revealed the disseminated presentation of large atypical lymphocytes (A, hematoxylin and eosin, ×600). Immunohistochemical staining revealed that the tumor cells were positive for CD3 (B, ×600) and CD30 (C, ×600). The patient received eight cycles of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone (CHOP) and achieved complete remission. Six months after the completion of CHOP chemotherapy, the first relapse was confirmed and the patient joined the Phase I study of oral forodesine.35 After 4 years of forodesine administration (100 mg, once daily), the patient experienced epigastric pain. Endoscopic examination revealed gastric ulcer lesions and a biopsy demonstrated the diffuse growth of large atypical lymphocytes (D, hematoxylin and eosin, ×400). Immunohistochemical staining revealed that the tumor cells were positive for CD20 (E, ×400). EBV early RNA 1 (EBER1) expression was detected in tumor cells by in situ hybridization (F, ×400). The patient was diagnosed with EBV-positive DLBCL. The patient received cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisolone (C-MOPP) in combination with rituximab, and subsequently achieved complete remission.