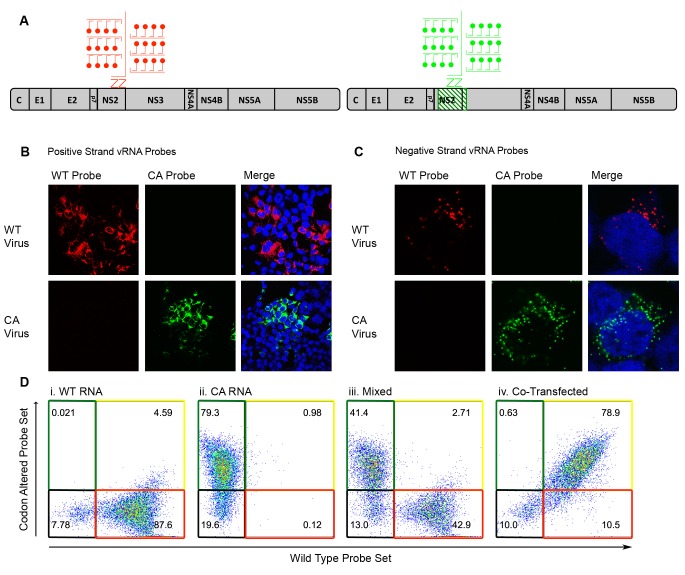
Figure 2. Differentiation of codon-altered and wild-type JFH1 using confocal microscopy and flow cytometry.
(A) RNA in situ hybridization probes were designed to differentiate between wild-type (WT) and codon-altered (CA) viral RNAs. These probes utilize branched DNA technology to amplify the contiguous DNA branches and not the RNA target itself. Roughly 8000 fluorophores labeled each target RNA. (B) Huh7.5.1 cells on coverslips were infected with WT or CA virus at MOIs of 0.01 FFU/cell. Cells were fixed after 72 hr, co-stained with WT and CA probe sets that recognized HCV positive strands and visualized by confocal microscopy. (C) Confocal microscopy of cells infected as in (B) but co-stained with probe sets to identify negative strands. (D) Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with WT RNA, CA RNA, or both by electroporation. Cells were fixed at 72 hr post transfection and costained with WT and CA RNA probe sets. Flow cytometry was performed on (i) cells transfected with WT RNA, (ii) cells transfected with CA RNA, (iii) a mixture of cells in i and ii, and (iv) cells transfected with both WT and CA RNAs.