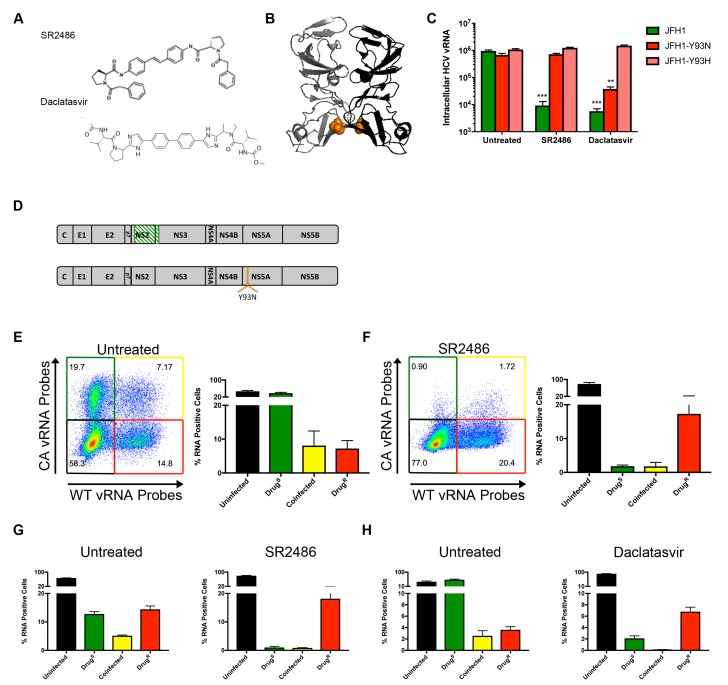
Figure 4. NS5A-resistant HCV is cis-dominant.
(A) Structures of SR2486 or Daclatasvir. (B) Structure of NS5A dimer with Y93 identified (orange). NS5A variants, Y93N and Y93H have previously been shown to confer drug resistance to multiple NS5A inhibitors. (C) Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with WT, WT-Y93N or WT-Y93H at MOI of 0.1 FFU/cell in the absence or presence of 500nM SR2486 or 50 nM Daclatasvir to determine the drug resistance profiles. (D) Diagram of CA virus with altered sequence (green hatches) and WT virus with location of Y93N mutation identified. (E/F) Huh7.5.1 cells were coinfected with CA and WT-Y93N for 72 hr followed by treatment with (F) or without (E) 500nM SR2486 as indicated for 24 hr and analyzed by flow cytometry. Results from four replicates of the experiment shown are quantified. (G) Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with CA and WT-Y93N at a MOI of 1 for 24 hr followed by treatment with DMSO or 500nM SR2486. Resistance to SR2486 was found to be cis-dominant. (H) Results from three replicate experiments in which Huh7.5.1 cells were coinfected with CA and WT-Y93H for 72 hr followed by treatment without (left) or with 50 nM Daclatasvir (right) are shown. Resistance to Daclatasvir was found to be cis-dominant.