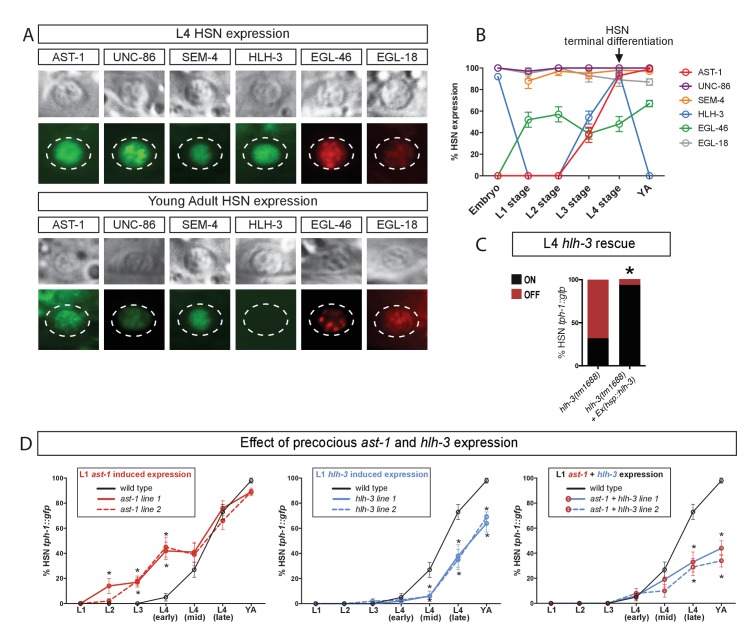
Figure 2. AST-1 acts as temporal switch for HSN maturation.
(A) Micrographs showing expression of the HSN TF combination at L4 larval stage and adult animals. (B) Analysis of HSN TF expression across all developmental stages in the HSN neuron. n > 30 cells for each developmental point. Error bars are SEP values. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for more detailed hlh-3 developmental expression. (C) Heat-shock-induced expression of hlh-3 at L4 larval stage is able to rescue tph-1::gfp expression defects in the HSN neuron. n > 100 cells per condition. See Source data 1 for primary data and Fisher's exact test p-values. *: p-value <0.05. (D) Precocious L1 onset of expression of ast-1, hlh-3 or both using an early active HSN-specific promoter (also expressed in NSM, ADF and VC4/5 neurons). Precocious ast-1 advances tph-1::gfp expression, while hlh-3 alone or in combination with ast-1 delays tph-1::gfp expression and produces expression defects. YA: young adult. n > 30 cells per time point and condition. See Source data 1 for primary data and Fisher's exact test p-values. *: p-value <0.05.