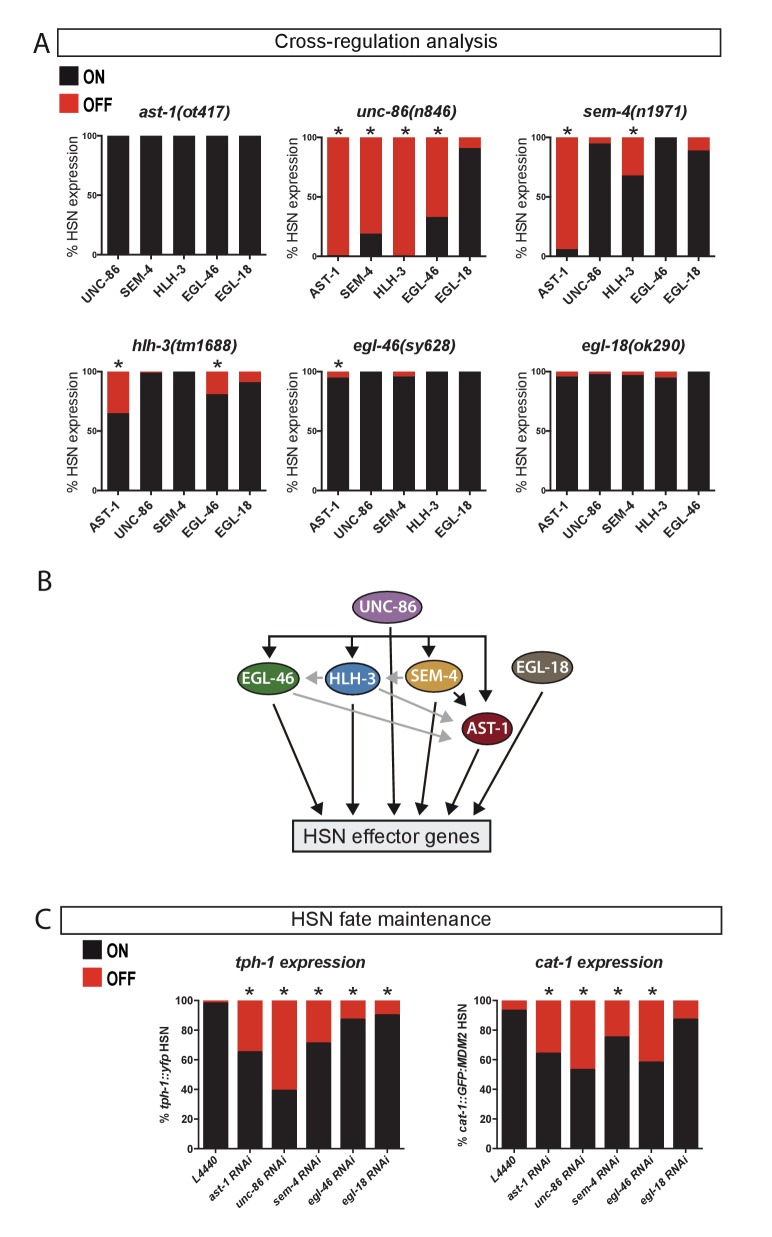
Figure 3. UNC-86 is a master regulator of the HSN transcription factor combination.
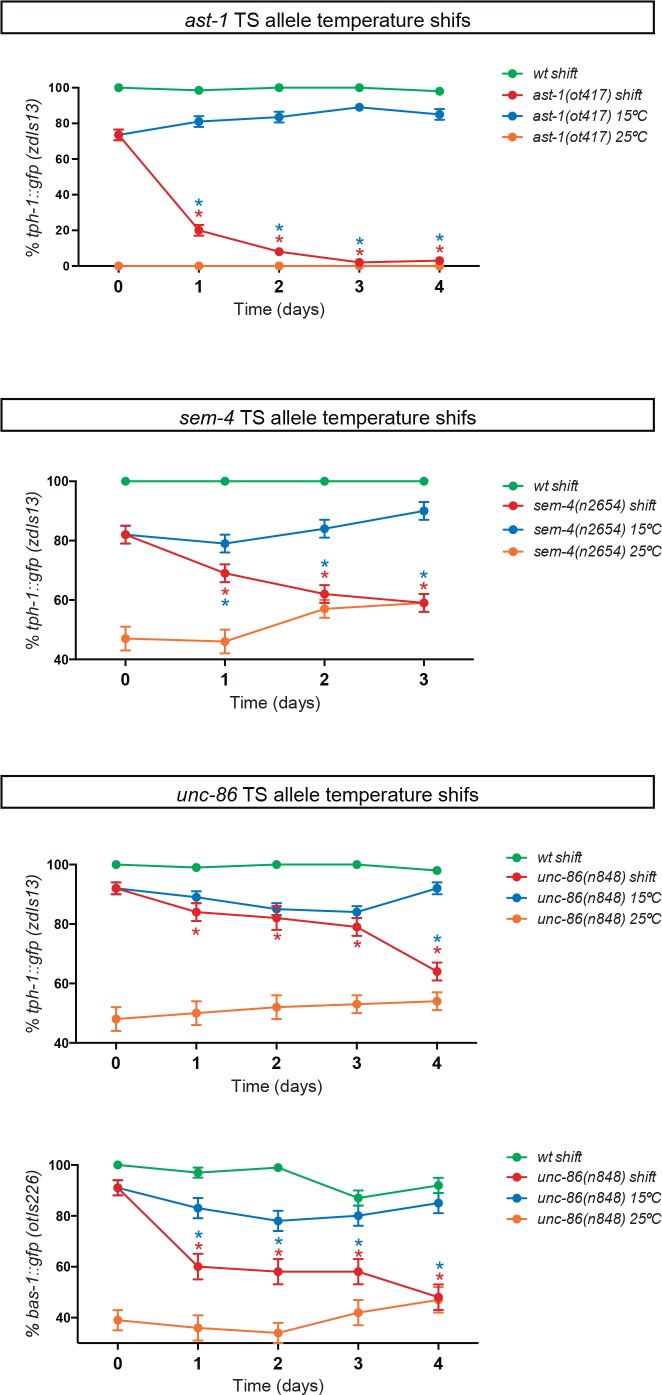
(A) Expression of the HSN TFs in different mutant backgrounds. All scorings were performed at adult stages except for HLH-3, where early L4 larvae were scored. Embryonic HLH-3 expression is unaffected in unc-86 mutants (data not shown). Graphs show the percentage of TF expression in mutant animals relative to wild type expression. n > 100 cells per condition, Fisher's exact test, *: p-value<0.05, See Source data 1 for raw data and exact p-values. (B) Summary of relationships among the HSN TF combination, black arrows mean strong effect (more than 50% loss of expression) and grey arrows depicts the rest of significant defects. (C) Loss-of-function (RNAi) experiments after HSN differentiation show that AST-1, UNC-86, SEM-4, EGL-46 and EGL-18 are required to maintain proper tph-1::yfp and cat-1::MDM2::gfp (unstable GFP) reporter expression. Worms were also scored prior to RNAi treatment to confirm correct HSN differentiation before starting the experiment. n > 100 cells per condition, Fisher's exact test, *: p-value <0.05. See Source data 1 for raw data and Figure 3—figure supplement 1 for maintenance analysis with temperature-sensitive alleles.