Figure 1. Summary of previously-characterized biotin biosynthetic pathway.
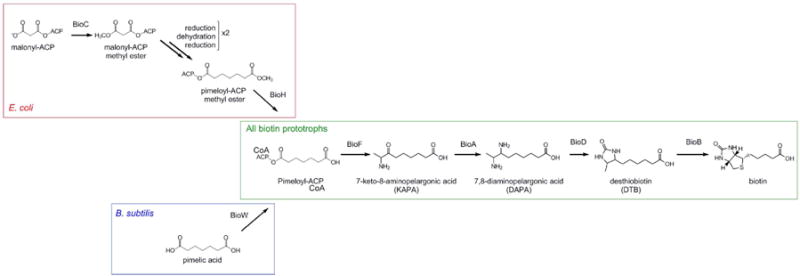
Late (green box) biotin biosynthesis is conserved in all biotin-synthesizing organisms and is catalyzed by the action of four enzymes: BioF, BioA, BioD, and BioB, which convert pimeloyl-ACP/CoA to biotin. Synthesis of the pimeloyl-ACP moiety differs between bacteria. In E. coli (red box), BioC methylates malonyl-ACP to form malonyl-ACP methyl ester, which then enters the fatty-acid elongation pathway. BioH demethylates pimeloyl-ACP methyl ester to form pimeloyl-ACP (Lin et al., 2010). In contrast, B. subtilis (blue box) utilizes BioI to break down long-chain fatty acids into pimeloyl-ACP. A secondary pathway exists in which free pimelic acid is converted to pimeloyl-ACP by BioW (Cryle, 2010).
