Figure 5. Pyruvate carboxylase catalytic activity is required for biotin prototrophy.
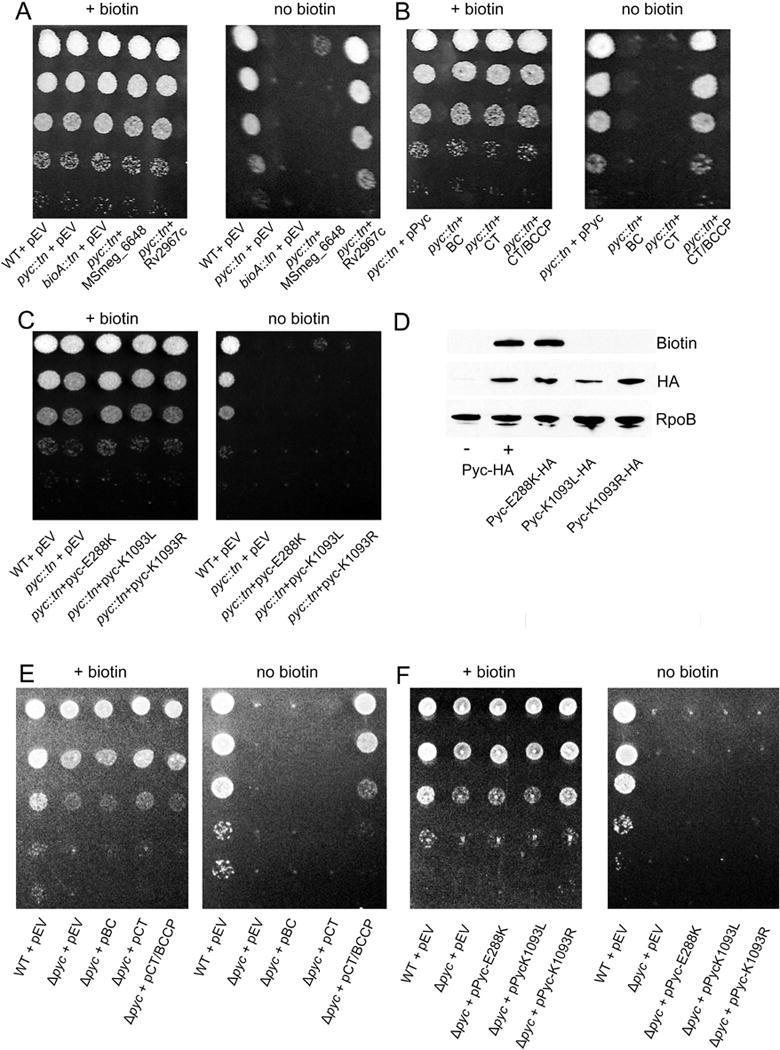
(A) TB Pyruvate carboxylase supports biotin biosynthesis. WT (MGM8019), pyc::tn (MGM8020), bioA::tn (MGM8021), and pyc::tn expressing either the annotated second pyruvate carboxylase in M. smegmatis (MSmeg_6648) (MGM8024) or the M. tuberculosis ortholog Rv2967c (MGM8025) for growth on medium lacking biotin. EV=empty vector (B) Truncation of Pyc. pyc::tn was complemented with plasmids expressing full length pyruvate carboxylase (MGM8023), biotin carboxylase (BC) domain (MGM8026), only the carboxytransferase (CT) domain (MGM8027), or the CT domain and the biotin-binding (BCCP) domains (MGM8028). (C) Pyruvate carboxylase BC active site or biotin attachment sites are required for biotin prototrophy. pyc::tn was complemented with plasmids expressing full length Pyc with a BC catalytic residue mutation (E288K) (MGM8029) or the essential residue for covalent attachment of biotin (K1093L/R) (MGM8030/8031). Each strain was N-terminally HA-tagged and expressed under the control of an ATc-dependent promoter. (D) Each of the Pyc isoforms from (C) as well as native pyruvate carboxylase (MGM8011) were N-terminally HA tagged. Expression of each of the mutants (E288K, K1093L/R) was similar to levels of native pyruvate carboxylase (Pyc-HA+) when induced with ATc. Low levels of pyruvate carboxylase were present in the absence of induction (Pyc-HA-). Detection of protein biotinylation was performed using streptavidin-HRP. RNA polymerase subunit B (RpoB) is shown as a loading control. Native pyruvate carboxylase (Pyc-HA) is the same strain shown in Fig. 2A and Fig. 4A. (E) Δpyc (MGM6521) was complemented with plasmids expressing the BC domain (MGM6522), only the CT domain (MGM6523), or the CT domain and BCCP domains (MGM6524). (F) Pyruvate carboxylase BC active site or biotin attachment sites are required for biotin prototrophy. Δpyc was complemented with plasmids expressing Pyc-E288K (MGM6525) or Pyc-K1093L/R (MGM6526/2527).
