Figure 5.
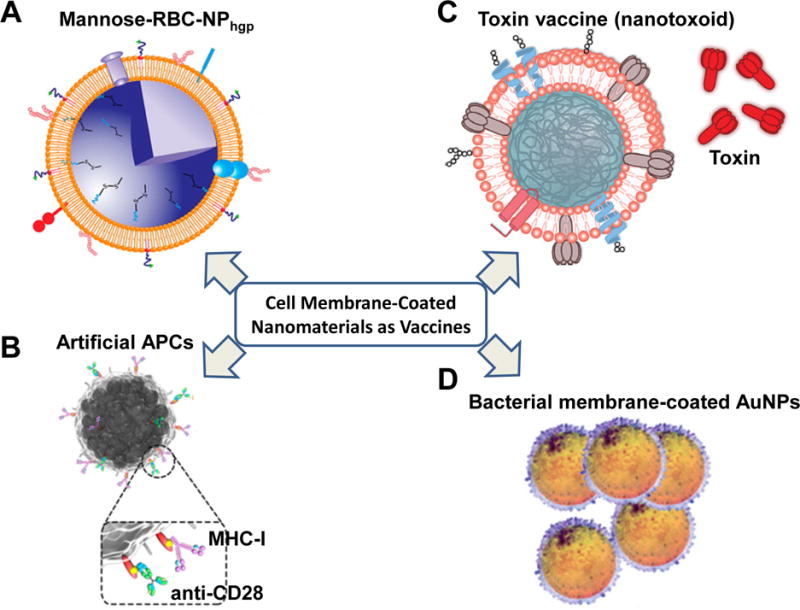
Cell membrane-derived nanomaterials for immunotherapy. (A) Mannose-RBC-NP vaccine for DC activation and tumor suppression. (B) Artificial magnetic APC vaccine for T cell stimulation and guided T cell tumor homing. The artificial APCs were magnetic nanocluster covered with leukocyte membranes and decorated with MHC-I and anti-CD28 for stimulating antigen-specific T cells. (C) Nanotoxoid for antitoxin vaccination. The Nanotoxoid was made of RBC membrane-coated NPs entrapping toxin. (D) Bacterial membrane-coated AuNPs for antibacterial immunity. (Adapted with permission from Ref 83, Copyright© 2015, ACS Publications; Ref 84, Copyright© 2017, ACS Publications; Ref 91, Copyright© 2013, Nature Publishing Group; and Ref 93, Copyright© 2015, ACS Publications.)
