Figure 5. Schematic model of polyamine-induced and eIF5A-mediated ribosomal queuing leading to enhanced initiation at the AUU start codon of the uCC on the AZIN1 mRNA.
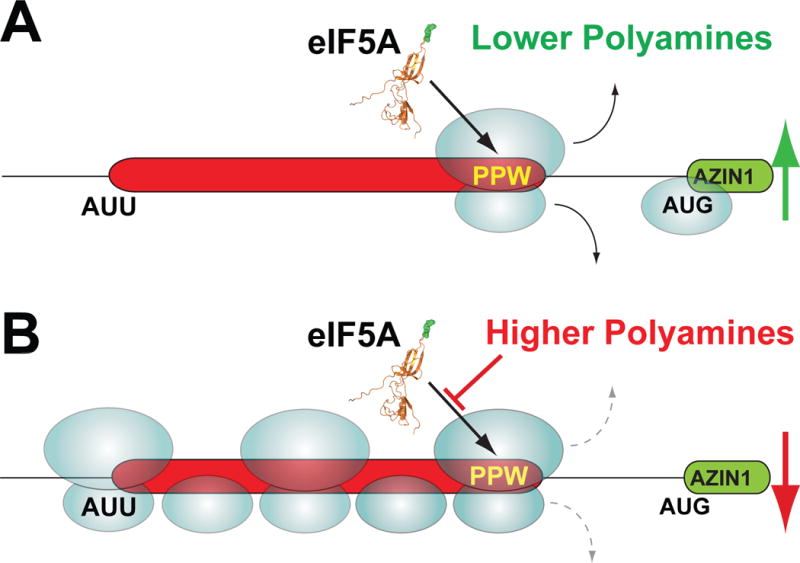
(A) Under conditions of lower polyamines most scanning 40S ribosomes skip over the uCC (red) start codon (AUU) without initiating and then initiate downstream on the AZIN1 mORF (green). The occasional ribosome that initiates on the uCC AUU start codon synthesizes the uCC peptide and then disengages from the mRNA. (B) Under conditions of higher polyamines any ribosome that initiates on the uCC start codon elongates down the uORF and encounters the PPW sequence. The high polyamines interfere with eIF5A function and cause the ribosome to stall. Subsequent scanning ribosomes, which mostly skip over the AUU start codon, and the occasional elongating ribosome form a queue behind the stalled ribosome. A queued subunit spends an extended time traversing and in the vicinity of the near cognate start codon allowing greater opportunities for initiation. The enhanced rate of initiation on the uCC reinforces the elongation stall, prevents ribosomes from scanning to the AZIN1 mORF, and effectively suppresses AZIN1 synthesis.
