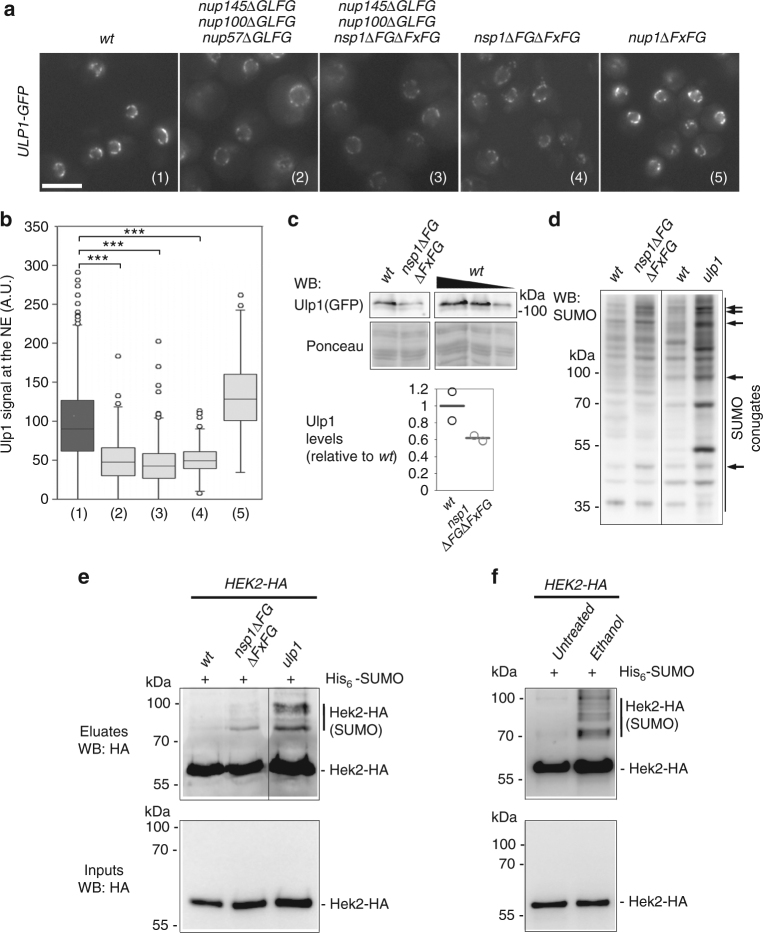
Fig. 4.
Defects in nuclear pore integrity impact Ulp1 activity and Hek2 sumoylation. a Fluorescence microscopy analysis of Ulp1-GFP in wt, nup145∆GLFG nup100∆GLFG nup57∆GLFG, nup145∆GLFG nup100∆GLFG nsp1∆FG∆FxFG, nsp1∆FG·FxFG and nup1∆FxFG cells grown at 30 °C. Scale bar, 5 µm. b Quantification of the Ulp1 nuclear envelope fluorescence intensity in the different strains. The numbers refer to the genotypes as depicted in (a). For each strain, at least 150 cells were analyzed. Boxplots were generated using KaleidaGraph (Synergy Software): each box encloses 50% of the measured values, the median is displayed as a line, and the bars extending from the top and bottom of each box mark the minimum and maximum values within the dataset falling within an acceptable range. Values falling outside of this range are displayed as individual points. ***P < 0.001 (Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test). c Ulp1-GFP amounts were measured in wt and nsp1∆FG∆FxFG cells by western blotting using anti-GFP antibodies (top panel). Ponceau staining was used as a loading control (lower panel). A serial dilution of the wt sample was used for quantification. Ulp1-GFP amounts normalized to ponceau are represented (mean and individual points, n = 2). d Whole cell extracts of the indicated strains were analyzed by western blotting using anti-SUMO antibodies. The bands that are modified in the nsp1∆FG∆FxFG mutant are also typically altered in ulp1 cells (arrows). e Hek2 sumoylation was detected in wt and nsp1∆FG∆FxFG cells as in Fig. 3. Total lysates (“Inputs”) and purified His-SUMO conjugates (“Eluates”) were analyzed by western blotting using anti-HA antibodies. The pattern of Hek2 sumoylation in ulp1 cells was analyzed as a control. The positions of the sumoylated and unmodified versions of Hek2-HA, as well as molecular weights, are indicated. f Hek2 sumoylation was similarly detected in wt cells, either untreated, or treated with 10% ethanol for 1 h