Fig. 1.
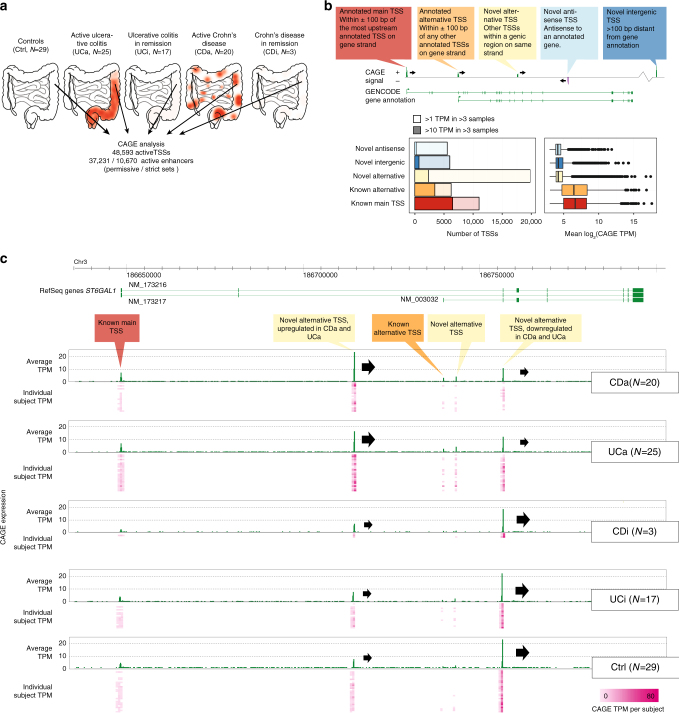
Defining the TSS landscape of IBD. a Overview of data set. Pinch biopsies from the descending colon were taken from 94 human subjects, classified into active ulcerative colitis (UCa), active Crohn’s disease (CDa), UC and CD patients in remission (UCi, CDi) and controls (Ctrl: subjects screened for IBD where all subsequent investigations turned out normal). For each biopsy, a CAGE library was produced, resulting in the detection of TSSs and enhancer regions. Schematics show the typical inflammatory patterns in the intestinal system, the approximate location of biopsy sampling and number of subjects in each group. b Detection and annotation of gene TSSs. Top panel shows an example gene with CAGE-defined TSSs, which are annotated as main, alternative or novel TSSs defined by their overlap with GENCODE gene annotation as indicated in callouts. CAGE-defined TSSs not falling into any of the categories were defined as novel intergenic TSSs. Left bottom panel shows the number of detected TSSs in each category (colors correspond to callouts in top panel), split by CAGE expression strength measured as tags per million (TPM). Right bottom panel shows the expression distribution of each category of TSSs as boxplots. c Genome-browser example of the detection of annotated and novel TSSs in the ST6GAL1 gene. From top to bottom, the browser plot shows the genomic location investigated, RefSeq gene annotation (exons are denoted as boxes, green indicate forward strand transcription). Below, CAGE TPM expression on the forward strand is shown as average across subjects (green bars) and for individuals (pink heat map, each row is one subject, columns are widened 5× for readability), split by subject group. Annotated and novel TSSs, annotated as in b are highlighted. Note that the first novel alternative TSS is upregulated in CDa and UCa vs. remaining groups, while the last novel alternative TSS has the opposite pattern (block arrows indicate TSSs and their overall strength in each subject group for these two TSSs). Conversely, the annotated TSSs are detected but not substantially changing between groups