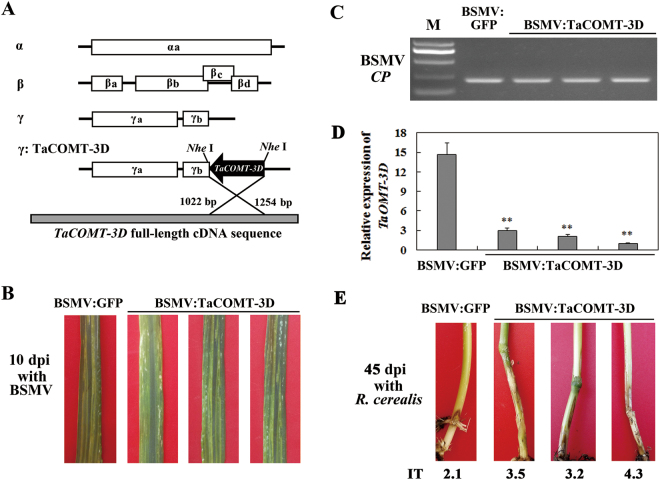
Figure 5.
Silencing of TaCOMT-3D by barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV)-induced gene silencing impairs CI12633 resistance to Rhizoctonia cerealis. (A) Scheme of genomic RNAs of BSMV construct and the construct of the recombinant virus expressing the wheat (Triticum aestivum) gene TaCOMT-3D, BSMV:TaCOMT-3D. The orientation of the TaCOMT-3D insert is indicated by dark boxes. (B) Mild chlorotic mosaic symptoms were observed on leaves at 10 days post inoculated (dpi) with BSMV: GFP or BSMV:TaCOMT-3D. (C) RT-PCR analysis of the transcription levels of BSMV coat protein encoding gene CP in the wheat plants infected by BSMV: GFP or BSMV:TaCOMT-3D at 10 dpi with R. cerealis. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of the transcription levels of wheat TaCOMT-3D gene in the wheat plants infected by BSMV: GFP or BSMV:TaCOMT-3D at after infection with R. cerealis. The relative transcript level of TaCOMT-3D in BSMV:TaCOMT-3D-infected (TaCOMT-3D-silencing) wheat CI12633 plants is relative to that in BSMV: GFP-infected (control) plants (set to 1). Significant differences were analyzed based on three replications (t-test: **P < 0.01). Error bars indicate standard deviation. (E) Sharp eyespot symptoms of the control and TaCOMT-3D-silencing CI12633 plants at 45 dpi with R. cerealis. IT indicates the infection type of wheat plant response to R. cerealis.