Figure 1.
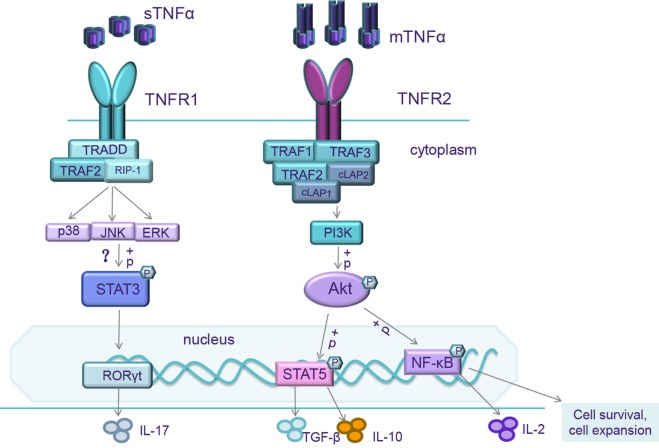
When mTNF/TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2) is activated, the intracellular domains recruit existing cytoplasmic TNF receptor-associated factor-2 (TRAF-2)–cIAP-1–cIAP-2 complexes resulting in the initiation of both canonical and non-canonical NF-κB/Rel and MAPK pathways activation. NF-κB/Rel and MAPK pathways activate IL-2 promoter and trigger IL-2 expression. NF-κB pathways also transcript genes associated with cell survival and cell proliferation. So, mTNF/TNFR2 signaling can enhance expansion and stability of Tregs and increase Treg sensitivity to low level of IL-2. It also activates the reciprocal PI3K/Akt pathway. Activation of Akt signaling impairs Th17 differentiation, correlated with an increased phosphorylation of STAT5 (143). When soluble TNFα (sTNFα)/TNFR1 is activated, the intracellular domains interact with TRADD, which receptor interacting protein-1 (RIP-1) and TRAF-2 to form Signal complex I, then further triggering extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The mechanisms of TNFR1 on Th17 differentiation are still unclear. These transcription factors might phosphorylate STAT3, upregulate the level of ROR-γt, and increase IL-17 production.