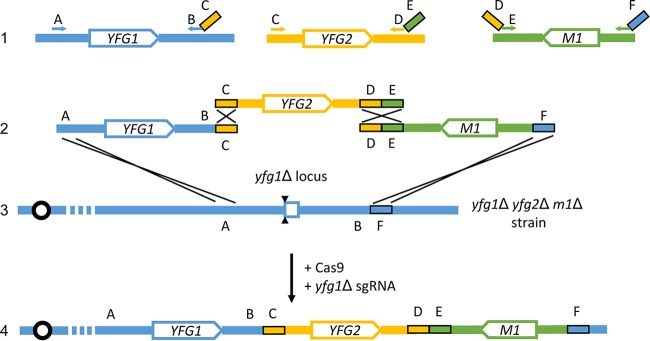
FIG 1 .
Strategy for concatemer assembly for rescue of mutant abilities (CARMA). Given a double mutant strain with the genotype yfg1Δ/Δ yfg2Δ/Δ with an available selectable marker M1, both YFG1 and YFG2 may conceptually be reintroduced at either the yfg1Δ (depicted in line 2 and line 3) or yfg2Δ locus. Cassettes containing YFG1 and YFG2 are generated by PCR from wild-type genomic DNA (line 1). The YFG1 cassette with sequences shown in blue is amplified with the primers indicated at the A and BC regions. It contains a segment of the YFG1 promoter, the YFG1 open reading frame (ORF), and terminator. Sequence C, containing homology to the YFG2 cassette, is introduced into the YFG1 cassette using the long primer indicated at the BC region. The YFG2 cassette with sequences shown in gold is amplified with the primers indicated at the C and DE regions. It contains a segment of the YFG2 promoter, the YFG2 ORF, and terminator. Sequence E, containing homology to the M1 marker cassette, is introduced into the YFG2 cassette using the long primer indicated at the DE region. The M1 marker cassette with sequences shown in green is amplified from a plasmid containing the M1 marker with the primers indicated at the DE and F regions. Sequence D, containing homology to the terminator region of YFG2, is introduced into the M1 cassette using the long primer indicated at the DE region. Sequence F, containing homology to a region downstream of YFG1 is introduced into the M1 cassette using the long primer indicated at the F region. All three cassettes are transformed into the yfg1Δ/Δ yfg2Δ/Δ m1Δ/Δ strain under M1 selection, along with DNA cassettes expressing CAS9 and a single guide RNA targeting the yfg1Δ locus. The double-strand break introduced by Cas9 complexed with the yfg1Δ targeting sgRNA is indicated by two black triangles. Expected homologous recombination events are depicted as single crosses, and together, they should yield a concatenated locus containing YFG1, YFG2, and M1 (line 4). Boxes C, D, E, and F each indicate segments of 80 bp. Where possible, homology between PCR cassettes is maximized. Sequences D and E together provide 160 bp of homology between the YFG2 and M1 cassettes. (In pilot experiments, we could not generate integrated concatemers with only 80 bp of homology between the YFG2 and M1 cassettes.) Sequences C and F provide 80 bp of homology to the YFG1 cassette and yfg1Δ locus, respectively. For construction of the ARG4:LEU2:HIS1 allele, the A-YFG1 interval provided 419 bp of homology. For construction of the UME6:BRG1:HIS1 allele, the A-YFG1 interval provided 403 bp of homology. In our experiments, we avoided extending the homology between the YFG1 and YFG2 cassettes to 160 bp in length by adding 80 bp of homology at sequence B. We were concerned that the presence of sequence B in the YFG2 cassette could allow integration of only YFG2 and M1 downstream of the yfg1Δ deletion scar in the B-F interval.