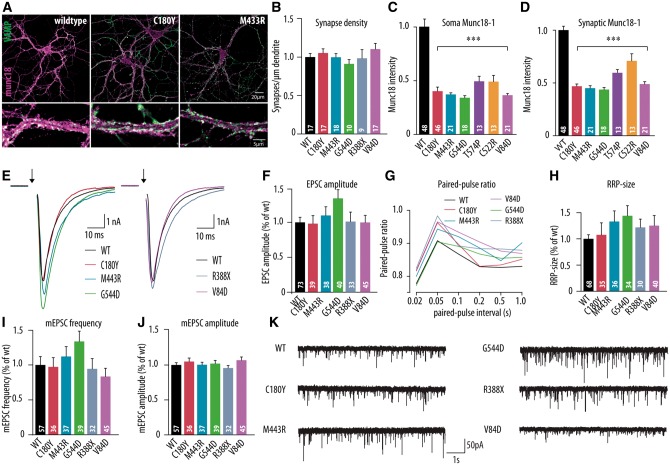
Figure 2.
Morphological and electrophysiological characteristics of dissociated hippocampal neurons expressing the human disease variants in Stxbp1+/− mouse neurons. (A) Dissociated cortical neurons were stained for Munc18-1 and synaptic marker synaptobrevin (VAMP). Examples represent Stxbp1+/− neurons expressing wild-type Munc18-1 (WT), C180Y or M433R human variants. (B–D) Morphological and synaptic characteristics of Stxbp1+/− neurons expressing wild-type Munc18-1 or one of the human disease variants: (B) mean synapse density: calculated as the ratio of synapse number and total dendritic length. (C and D) Mean somatic and synaptic Munc18-1 level. (E) Example traces of evoked release upon a single action potential stimulation from Stxbp1+/− neurons expressing wild-type Munc18-1, C180Y, M433R, V84D, G544D or R388X human variants. (F) Mean EPSC amplitude expressed as the ratio of the infected wild-type values. (G) Paired-pulse ratio (second EPSC/first EPSC) depending on the pulse interval. (H) Readily releasable pool estimate derived from back-extrapolation of cumulative total charge released during 40 Hz train, 100 APs (I) Frequency of spontaneous release expressed as the ratio of infected wild-type values. (J) Amplitude of spontaneous release expressed as the ratio of infected wild-type values. (K) Example traces of spontaneous release in Stxbp1+/− neurons expressing wild-type Munc18-1, C180Y, M433R, G544D, R388X or V84D human variants. The number of analysed cells is indicated in the bars. ***P < 0.001 versus infected wild-type control. mEPSC = mini excitatory postsynaptic current; RRP = readily releasable pool.