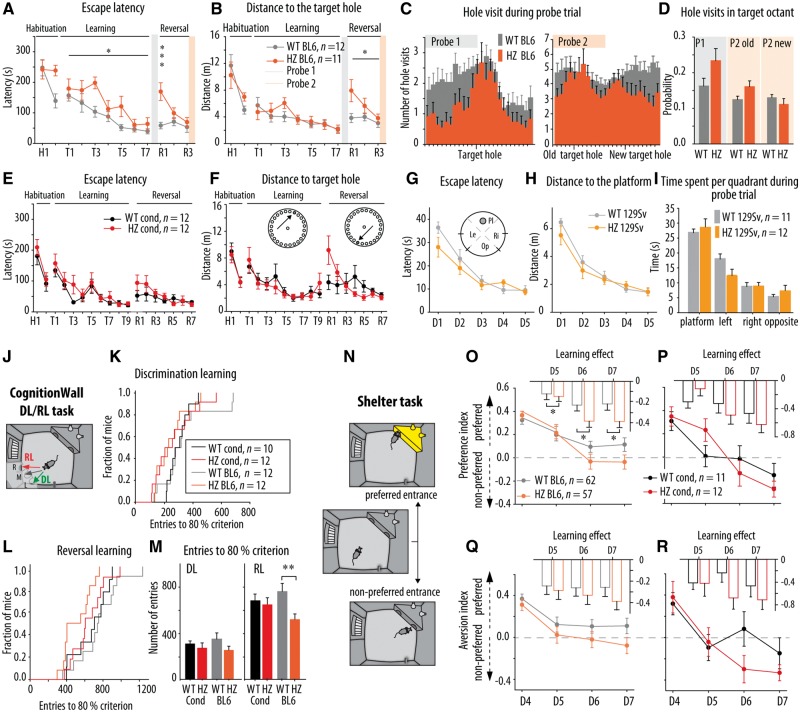
Figure 7.
Learning and memory in Stxbp1+/− mice in classical spatial paradigms and recently developed automated tasks in the PhenoTyper. (A and B) Latency and distance travelled to find the escape hole in the Barnes maze during the learning phase for congenic BL6 Stxbp1+/− mice. Congenic BL6 Stxbp1+/− (HZ BL6) showed longer latency to find new escape hole during the learning phase (P = 0.026) and during R1 (P < 0.001) and travelled longer distance to the new escape hole (R1-R3: P = 0.024) compared to their controls (WT BL6). (C) HZ BL6 mice showed narrower distribution of holes visit around the target hole during the first probe trial (P1) compared to wild-type BL6. (D) Probability of hole visits in the old target octant during the P1 and P2 tended to be higher for HZ BL6 mice compared to their controls (P = 0.086 and P = 0.060, respectively) and there were no differences in the probability of hole visits in the new target octant during the P2. (E and F) Latency and distance travelled to find the escape hole in the Barnes maze during the learning phase were similar for Stxbp1cre/+ mice (HZ cond) and their controls (wild-type cond). (G and H) Escape latency and distance travelled to the platform during the training in the Morris water maze was similar for reverse 129Sv Stxbp1+/− mice and control mice. (I) Time spent per quadrant during the probe trial was similar for reverse 129Sv Stxbp1+/− mice and control mice. (J) Schematic overview of the CognitionWall DL/RL task. (K and L) Kaplan-Meier survival curves shows the fraction of congenic BL6 and conditional Stxbp1 mice that reached the 80% criterion as a function of hole entries during the DL and RL phases. (M) Average number of entries made per group to reach 80% criterion during the DL and RL phases. HZ BL6 mice reached the 80% criterion during RL with lower number of entries compared to control (P = 0.004). (N) Schematic overview of the Shelter task protocol in the PhenoTyper to assess avoidance learning. (O and P) The preference index during the dark phases of the avoidance learning task was similar for HZ BL6 and HZ cond mice and their controls. Insets represent the learning effect on the preference index (D5/D6/D7-D4). The insets in graph O shows that congenic BL6 Stxbp1+/− mice showed a stronger learning effect compared to their controls (P = 0.012). (Q and R) The aversion index during the dark phases of avoidance learning task showed trend toward lower values for HZ BL6 mice compared to their controls (P = 0.101). The aversion index was similar between HZ cond mice and their controls. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared to respective control. Statistical analysis is explained in the Supplementary material.