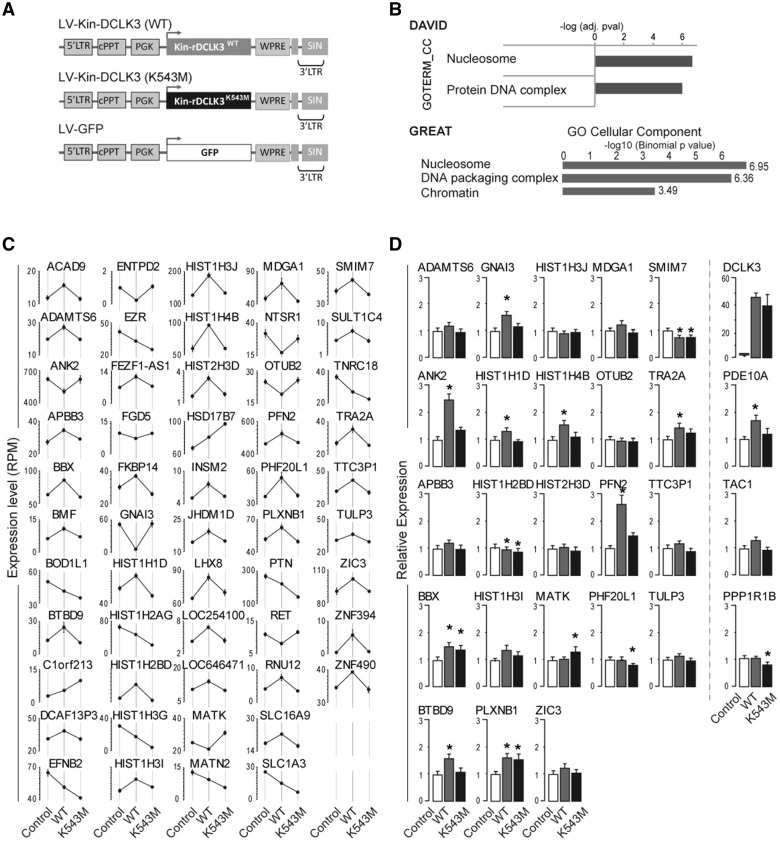
Figure 6.
Effect of rDCLK3 kinase domain in human striatal neurons. (A) Schematic representation of the lentiviral (LV) constructs used to transduce human striatal neurons derived from neuronal stem cells for transcriptomic analysis of the effects of the rDCLK3 kinase domain by AmpliSeq at 12 days post-infection. (B) Gene ontology analysis of genes (n = 88) significantly upregulated by Kin-rDCLK3WT using DAVID and GREAT identified functions related to nucleosome and chromatin/DNA remodelling. (C) Genes with significant changes in expression dependent on the catalytic activity of Kin-rDCLK3 (i.e. genes displaying significant differences in expression (FDR < 0.05) between Kin-rDCLK3WT and GFP and between Kin-rDCLK3K543M and Kin-rDCLK3WT). (D) Expression levels of a subset of genes identified in C in human neurons expressing Htt171-82Q and either GFP, Kin-rDCLK3WT or Kin-rDCLK3K543M. Expression levels where determined by RT-qPCR. Results are expressed as means (C, n = 4 wells per group; D, n = 5–6 wells per group) ± SEM. One-way ANOVA factorial analysis in D followed by Fisher’s post hoc PLSD test. *P < 0.05.