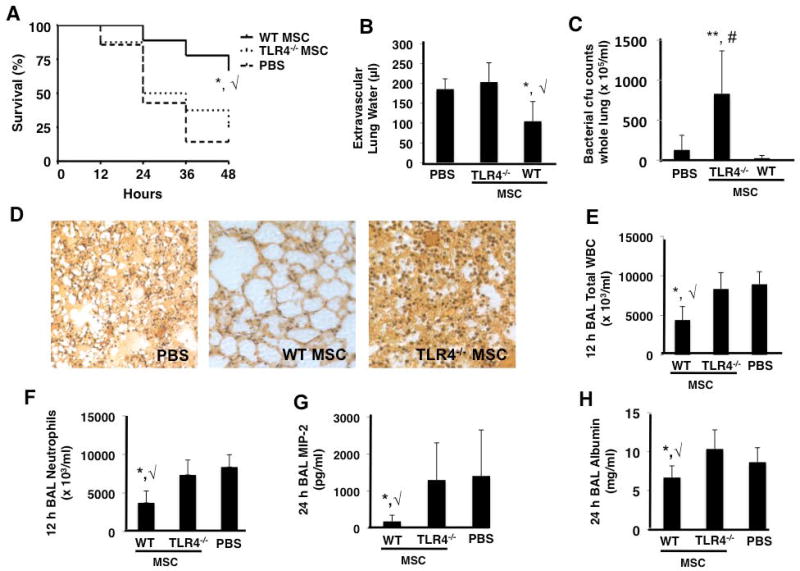
Figure 2. TLR4 −/− MSCs exhibit no therapeutic effects in the in vivo E. coli pneumonia model.
TLR4 −/− MSCs did not improve survival (A), lung edema (B), or bacterial burden (C) as compared to PBS treated mice at 48 h (panels A and B, *, √ p < 0.05 for WT MSC vs PBS and TLR4 −/− MSC groups, respectively; panel C, **, # p < 0.01 for TLR4 −/− MSC vs WT MSC and PBS treated groups, respectively; n = 15 – 20 per group). Lung histology also demonstrated that TLR4 −/− MSC treated mice had no appreciable decrease in lung damage versus PBS treated mice (D). BAL at 12 h post-infection demonstrated that TLR4 −/− MSCs did not reduce inflammatory cell influx into the alveolar space (panels E and F, *, √ p < 0.05 for WT MSC vs PBS and TLR4 −/− MSC groups, respectively, n = 4 per group). At 24 h post-infection, BAL studies showed that TLR4 −/− MSCs did not reduce the levels of the inflammatory cytokine, MIP-2, or the albumin concentration (G and H, respectively, *, √ p < 0.05 for WT MSC vs PBS and TLR4 −/− MSC groups, n = 6–9 per group).