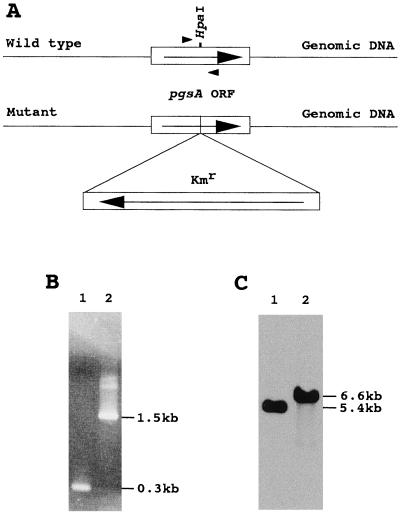
Figure 2.
Insertional mutagenesis of the pgsA gene of Synechocystis sp. A, Structure of the pgsA gene in the wild type and the insertional mutant of Synechocystis sp. The directions of transcriptions of Kmr and the pgsA gene are indicated by arrows. B, PCR analysis of the pgsA gene in the wild type (lane 1) and the pgsA mutant (lane 2). The positions of DNA size markers are indicated on the right. The positions of the primers used for PCR reactions were shown by arrowheads in Figure 2A. C, Southern hybridization analysis of the pgsA gene in the wild type (lane 1) and the pgsA mutant (lane 2). Genomic DNAs extracted from the wild type and the pgsA mutant cells were digested with XbaI. One microgram of DNA was applied to each lane. The membrane was hybridized at 42°C using the pgsA gene of Synechocystis sp. as a DNA probe.