Figure 5. VTA-Area X Terminal Manipulations Do Not Have Motor or Motivational Effects on Song.
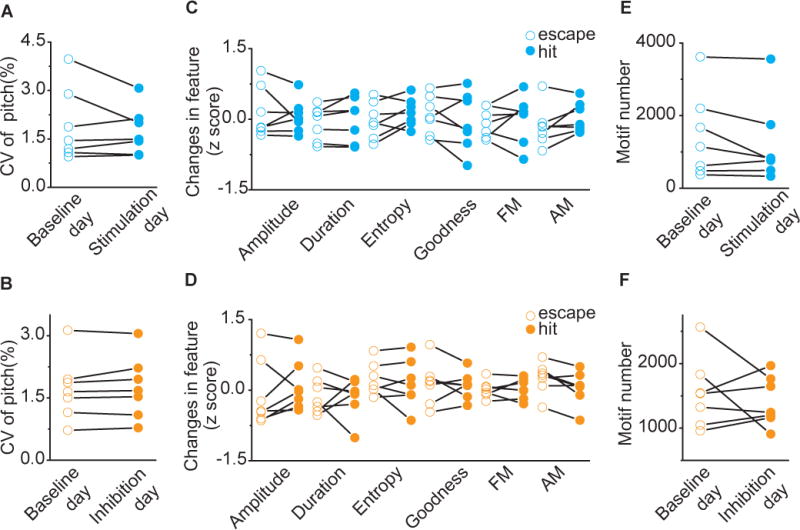
A) Variability in pitch of target syllables for baseline day (open, CV = 1.91±0.42%) and stimulation day (filled, CV = 1.73±0.27%). Closed-loop optical stimulation of target syllables did not change the coefficient of variation of syllable pitch of target syllables (p=0.81, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test). B) Variability in pitch of target syllables for baseline day (open, CV = 1.71±0.29%) and inhibition day (filled, CV = 1.75±0.28%). Closed-loop optical inhibition of target syllables did not change variability in pitch of target syllables (p=0.47, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test). C) Spectral characteristics of ‘hit’ (filled) and ‘escape’ (open) syllable during the first stimulation session (200 motifs). Across experiments (n=7), there were no differences in amplitude (p=0.69), duration (p=0.30), Weiner entropy (p=0.16), goodness (p=0.38), frequency modulation (FM, p=0.69) and amplitude modulation (AM, p=0.11, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) between ‘hit’ and ‘escape’. D) Spectral characteristics of ‘hit’ (filled) and ‘escape’ (open) syllable during the first inhibition session (200 motifs). Across experiments (n=7), there were no differences in amplitude (p=0.38), duration (p=0.81), Weiner entropy (p=0.81), goodness (p=0.93), frequency modulation (FM, p>0.99) and amplitude modulation (AM, p=0.078, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test) between ‘hit’ and ‘escape’. E) Motif number for baseline day (open, 1,444 ±441 motifs) and stimulation day (filled, 1,215 ±425 motifs). Closed-loop optical stimulation of target syllables didn’t change singing rate (p=0.15, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test). F) Motif number for baseline day (open, 1,544 ±204 motifs) and inhibition day (filled, 1,413 ±144 motifs). Closed-loop optical inhibition of target syllables didn’t change singing rate (p>0. 999, n=7, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test).
