Figure 7. Spectral and Temporal Precision of Optically Directed Changes in Song.
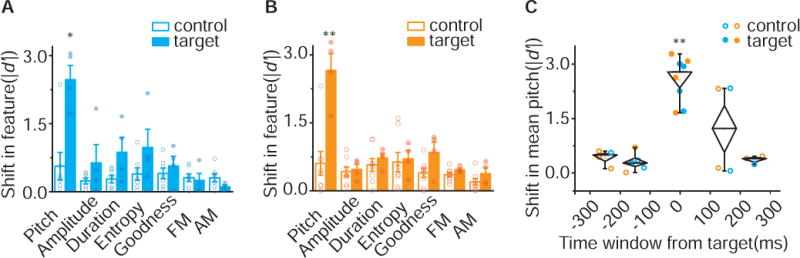
A) Shift in song spectral features for target (filled) and control (open) syllables of axChR2 birds (n=4). Changes in song were restricted to the pitch of target syllables (p=0.024, Mann-Whitney test). Spectral characteristics including amplitude (p=0.65), duration (p=0.11), Weiner entropy (p=0.11), goodness (p=0.53), FM (p=0.72), and AM (p=0.16) were not altered for either target or control syllables. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. B) Shift in song spectral features for target (filled) and control (open) syllables of axArchT birds (n=4). Changes in song were restricted to pitch of target syllables (p=0.0081, Mann-Whitney test). Spectral characteristics including amplitude (p=0.68), duration (p=0.46), Weiner entropy (p=0.57), goodness (p=0.15), FM (p=0.21), and AM (p=0.15) were not altered for either target or control syllables. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. C) Shift in mean pitch for target (filled) and control (open) syllables from both axChR2 birds (blue, n=4) and axArchT+ birds (orange, n=4) at millisecond time scale. Changes in pitch are restricted to target syllables (ANOVA, F4,19 = 13.62, P < 0.05, the diamonds denote s.e.m. and whiskers denote the 10–90% range). See also Figure S6.
