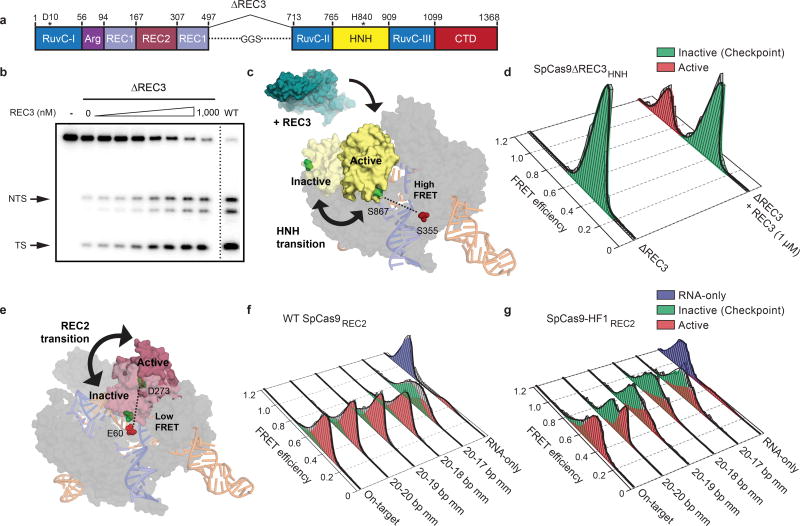
Figure 2. The alpha-helical lobe regulates HNH domain activation.
a, Domain organization of SpCas9ΔREC3. b, On-target DNA cleavage assay using SpCas9ΔREC3 with increasing concentrations of the REC3 domain supplied in trans, resolved by denaturing PAGE; repeated three independent times with similar results. c, Schematic of SpCas9ΔREC3HNH, with REC3 added in trans. Inactive to active structures represent HNH in the sgRNA-bound (PDB ID: 4ZT0) to dsDNA-bound (PDB ID: 5F9R) forms, respectively. d, smFRET histograms showing HNH conformation with SpCas9ΔREC3HNH bound to an on-target substrate, with and without REC3. e, Schematic of SpCas9REC2; HNH domain is omitted for clarity. Inactive to active structures represent REC2 in the sgRNA- (PDB ID: 4ZT0) to dsDNA-bound (PDB ID: 5F9R) forms, respectively. f–g, smFRET histograms showing REC2 conformation with f, WT SpCas9REC2 and g, SpCas9-HF1REC2 bound to on-target and mismatched targets. For panels d, f and g, black curves represent a fit to multiple Gaussian peaks.