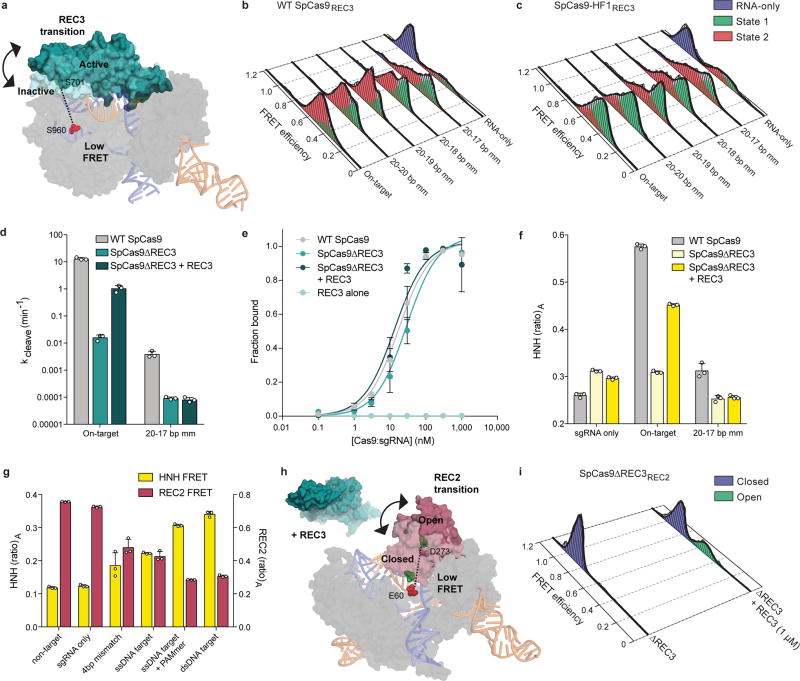
Extended Data Figure 4. Nucleic acid sensing requires engagement with the REC3 domain and outward rotation of the REC2 domain.
a, Schematic of SpCas9REC3 with FRET dyes at positions S701C and S960C, with HNH domain omitted for clarity. Inactive to active structures represent REC3 in the sgRNA-bound (PDB ID: 4ZT0) to dsDNA-bound (PDB ID: 5F9R) forms, respectively. b–c, smFRET histograms showing HNH conformational activation with black curves representing a fit to multiple Gaussian peaks for b, WT SpCas9REC3 and c, SpCas9-HF1REC3 bound to perfect and PAM-distal mismatched targets. The purple peak denotes the sgRNA-only bound state, while the red and green peaks represent two states of REC3 with conformational flexibility upon binding to DNA substrates. d, REC3 in vitro complementation assay with SpCas9ΔREC3 by measuring cleavage rate constants. e, On-target DNA binding assay in the presence or absence of the REC3 domain; mean and s.d. shown. f, REC3 in vitro complementation assay with SpCas9ΔREC3 by measuring HNH activation with (ratio)A values. g, (Ratio)A data with SpCas9REC2 and SpCas9HNH showing reciprocal FRET states with the indicated substrates. For panels d–g, mean and s.d. shown; n = 3 independent experiments (overlaid as white circles in panels d, f, and g). h, Schematic of SpCas9ΔREC3REC2 with FRET dyes at positions E60C and D273C, with the REC3 domain added in trans. Inactive to active structures represent REC2 in the sgRNA-bound (PDB ID: 4ZT0) to dsDNA-bound (PDB ID: 5F9R) forms, respectively. i, smFRET histograms measuring REC2 conformational states with SpCas9ΔREC3REC2 in the absence and presence of the REC3 domain when bound to an on-target substrate.