Figure 3. Acquired PARPi resistance is associated with RAS/MAPK pathway activation and sensitization to the combination of MEKi and PARPi.
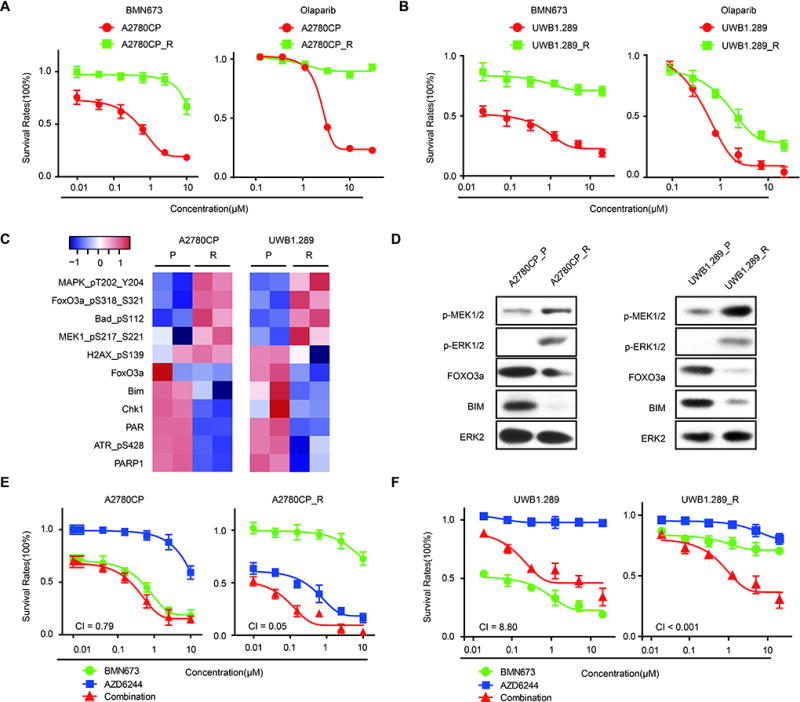
(A) Drug response curves of BMN673 (left) or olaparib (right) in parental or PARP inhibitor-resistant A2780CP incubated with indicated doses for 96 hours.
(B) Drug response curves of BMN673 (left) or olaparib (right) in parental or PARP inhibitor-resistant UWB1.289.
(C) Heatmap of differentially expressed proteins from RPPA of A2780CP _R and UWB1.289_R compared to parent cells, indicating consistent RAS/MAPK pathway activation and decreased FOXO3a, BIM, and PARP1 in both PARPi-resistant cell types.
(D) Western blot validation of RAS/ERK signaling (pMEK, pERK), FOXO3a, and BIM in both PARPi resistant and sensitive cell lines.
(E–F) Drug response curves of parental or PARP inhibitor-resistant A2780CP (E) or UWB1.289 (F) cells treated for 96 hrs with various concentrations of PARPi (BMN673) combined with MEKi (AZD6624).
