Figure 3.
HOXB4 Does Not Alter Blast Colony-Forming Cell (Hemangioblast) Frequencies
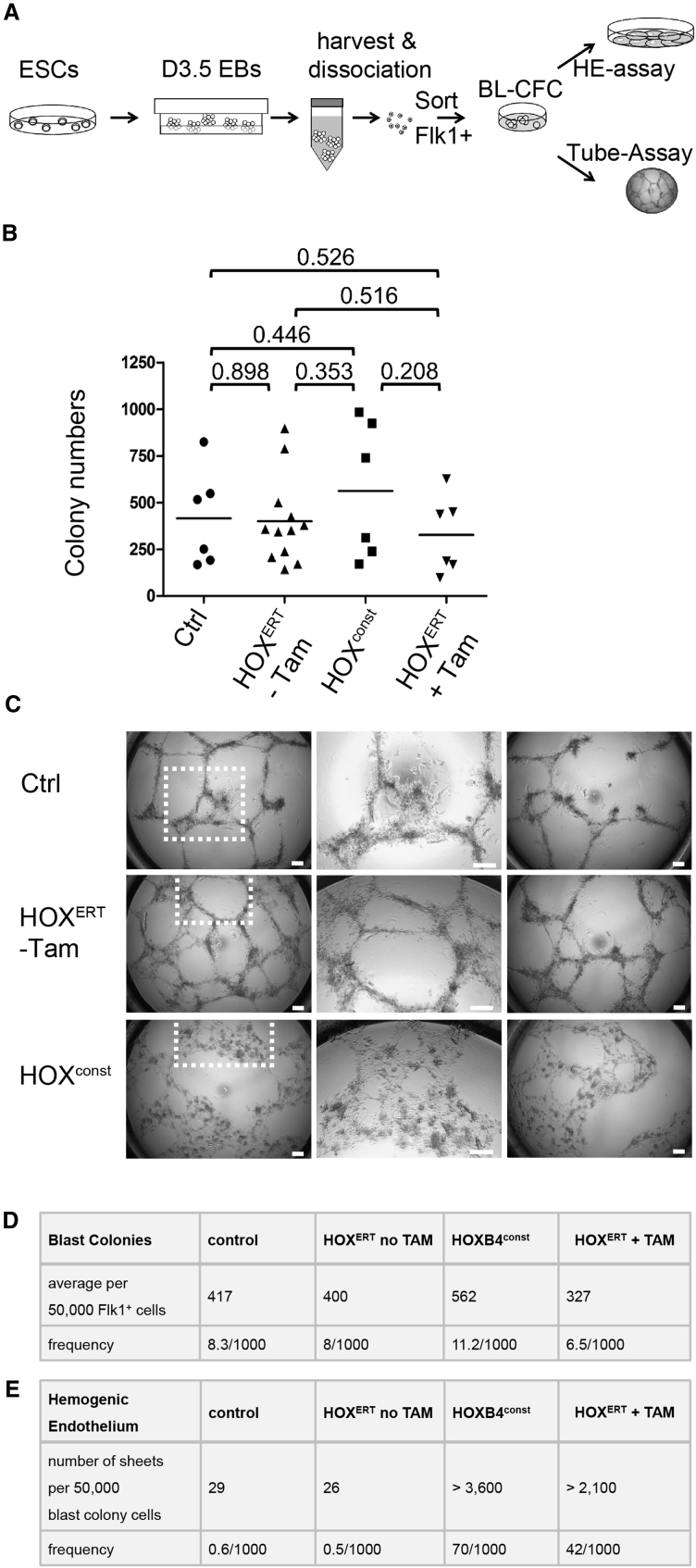
(A) Depicted is an overview of FLK-1+ hemangioblast frequency determination, subsequent HE quantitation, and evaluation of tube formation propensities. iRunx cells were differentiated as EBs for 3.5 days, FLK-1+ cells with and without ectopically expressed HOXB4 were sorted, and 50,000 cells each subjected to blast colony-forming assays to retrospectively quantify the number of hemangioblasts 4 days later. All colonies were harvested, dissociated, and 50,000 cells each placed onto OP9 stroma cells to determine the number of HE colony-forming progenitors 3 days later. A total of 40,000 cells each were placed into a Matrigel-based tube formation assays. All assays were performed at least in triplicate, without Runx1 induction.
(B) Ectopic HOXB4 expression did not significantly alter the total number of colonies. For statistical analysis, p values were calculated based on the two-sided, unpaired Student's t test, n = 6–12; the significance level was defined as p < 0.05. The individual colony numbers are shown as symbols, the arithmetic means depicted as lines.
(C) HOXB4 altered the ability of blast colony cells to form tubes. Instead of the small, thin tubular network observed in the controls (Ctrl and HOXB4ERT without Tam), flat, adherent structures were formed with differing morphologies. The mid-panels show magnifications of the areas indicated in the left pictures. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(D and E) Frequencies of BL-CFCs (arithmetic means, as described in B) (D) and of HE colonies (arithmetic means of n = 3 independent replicates) without HOXB4 induction (HOXB4ERT no Tam) or with constitutively expressed (HOXB4 const) or induced HOXB4 (HOXB4ERT + Tam) (E).