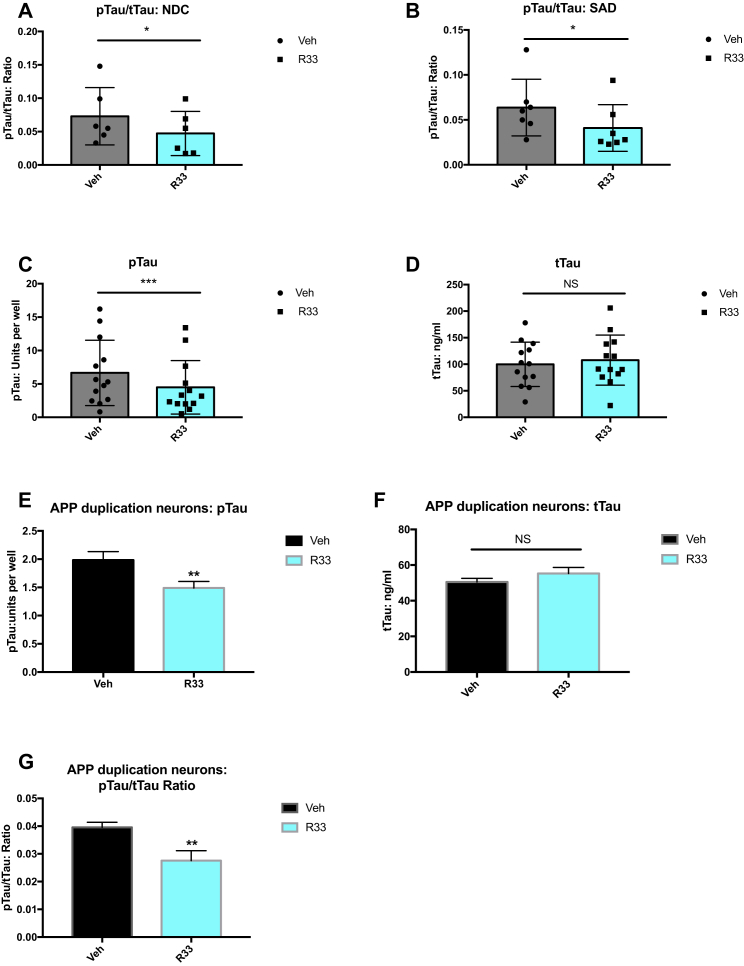
Figure 3.
Retromer Stabilization Reduces the pTAU/tTAU Ratio in hiPSC-Derived Neurons
(A) pTAU/tTAU ratio in purified neurons derived from NDC individuals treated with vehicle (dots) or R33 (squares) for 72 hr. n = 6 NDC individuals (represented by dots/squares); two to four independent experiments/individual/treatment.
(B) pTAU/tTAU ratio in purified neurons derived from NDC (SAD) individuals treated with vehicle (dots) or R33 (squares) for 72 hr. n = 7 SAD individuals (represented by dots/squares); two to four independent experiments/treatment.
(C) R33 reduces the TAU ratio by lowering phosphorylated TAU on Thr 231 in all samples (NDC and SAD neurons). n = 13 individuals (SAD + NDC) represented by dots/squares; two to four independent experiments/treatment.
(D) Levels of tTAU in all samples (NDC and SAD neurons) are unaffected by R33 treatment. n = 13 individuals (SAD + NDC) represented by dots/squares; two to four independent experiments/treatment.
(E) R33 reduces pTAU (Thr 231) in hiPSC neurons derived from an APP duplication patient.
(F) R33 does not affect tTAU levels in APP duplication neurons.
(G) R33 decreases the pTAU/tTAU ratio in APP duplication neurons.
Non-normally distributed data (A–D) were analyzed by Wilcoxon test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. NS, nonsignificant. Error bars represent SD. (E–G) For APP duplication: n = 1 FAD individual, three independent experiments/treatment. For each comparison, a two-tailed t test was performed. ∗∗p < 0.01. NS, nonsignificant. Error bars represent SD. See also Figure S3.