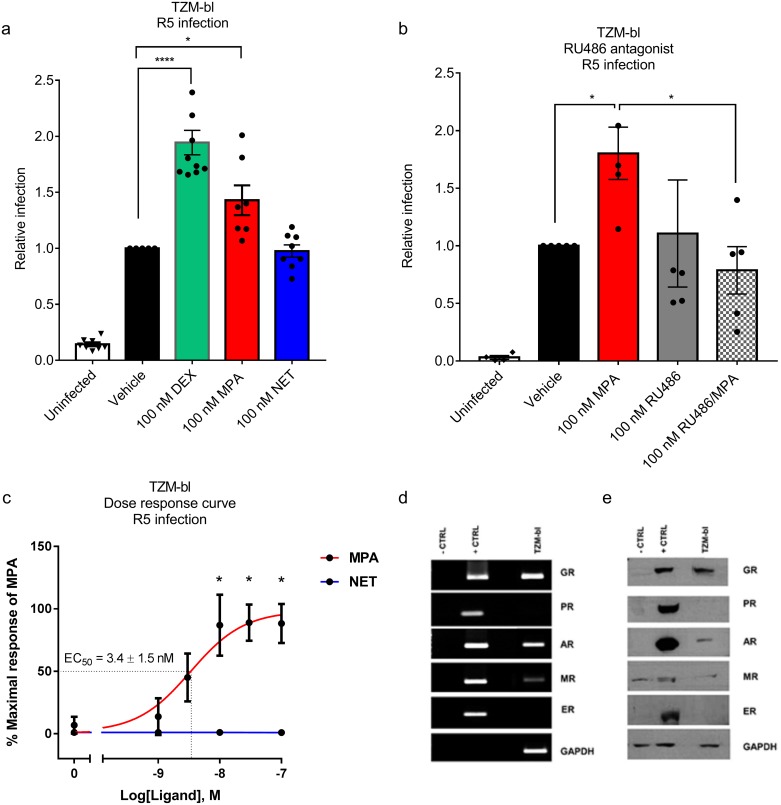
Fig 4. MPA, unlike NET, dose-dependently increases R5 HIV-1 replication in the TZM-bl cervical cell line, via a GR-dependent mechanism.
TZM-bl cells were stimulated in parallel for 24 hours with the various ligands, or combinations thereof or vehicle control (0.1% v/v EtOH), at the concentrations indicated, before infection with 20 IU/mL R5 HIV-1BaL-Renilla. Samples were harvested 48 hours later for Renilla luciferase and MTT viability assays. Each condition was performed at least in triplicate. Relative infection was calculated by normalising RLU against corresponding MTT values. This value for vehicle was set to 1 for (a) and (b), while for (c), data were analysed relative to the maximal response generated by MPA which was set to 100%. Statistical analysis was performed using (a) a parametric one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post test when comparing to vehicle or (b) a non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA with a subsequent unpaired t test comparing vehicle and MPA or comparing MPA and MPA/RU486. (c) A non-linear regression line was generated to calculate EC50 and statistical analysis was performed using a parametric one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons post-test comparing all conditions. Significant differences are shown by *, ** or *** denoting p<0.05, p<0.01 or p<0.001, respectively. The data (a-c) are represented as mean ± SEM and show the results of nine, five and six independent experiments, respectively, with each point performed in triplicate at least. (d-e) The GR is the predominant steroid receptor protein expressed in the TZM-bl cell line. Cell lysates were prepared and the steroid receptor mRNA and protein levels were detected by qRT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. (d) indicates that TZM-bl cells express detectable GR, AR and MR mRNA while (e) shows that TZM-bl cells express detectable GR and AR protein.