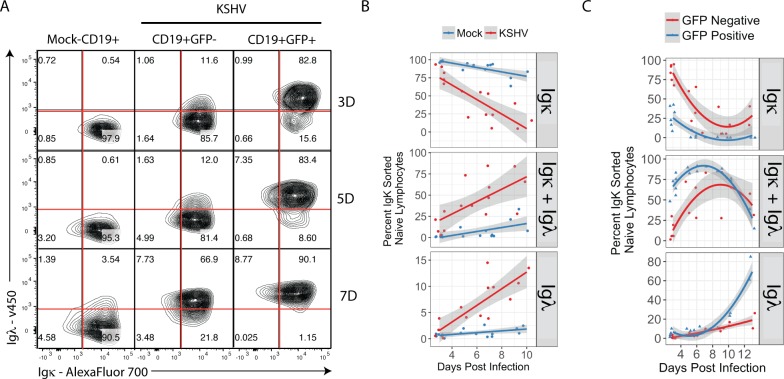
Fig 4. KSHV-infected Igκ+ lymphocytes become Igλ+ via an isotypically included intermediate.
Primary naïve B lymphocytes were magnetically sorted from total tonsil lymphocytes, then subsequently flow sorted based on light chain expression and infected with KSHV or mock-infected. At 3, 5 and 7 days post-infection 2e5 cells were removed from each culture and analyzed by FCM for expression of Igκ and Igλ. (A) FCM plots gated as shown in S2A Fig from a representative experiment. (B) Aggregate data for 6 experiments from 6 individual tonsil specimens showing the percent of the single, viable, CD19+ population with each light chain phenotype (Igκ+, Igκ+Igλ+ and Igλ+) based on gates shown in (A) over the time course of infection. Linear regression on the aggregate data was performed in R software using least means method and gray shading represents a 95% confidence interval. Additional linear mixed model regression on each independent experiment followed by ANOVA (Type II Wald F test with Kenward-Roger df) analysis revealed highly significant and dominant effects of KSHV infection for each light chain immunophenotype (for Igκ: F = 58.05, p = 5.8E-8; for Igκ+Igλ: F = 27.95, p = 1.8E-5; for Igλ: F = 35.06, p = 3.5E-6). (C) Aggregate data as in (b) for KSHV-infected samples only separating GFP+ and GFP- events. Biexponential regression was performed in R software using least means method and gray shading represents a 95% confidence interval.