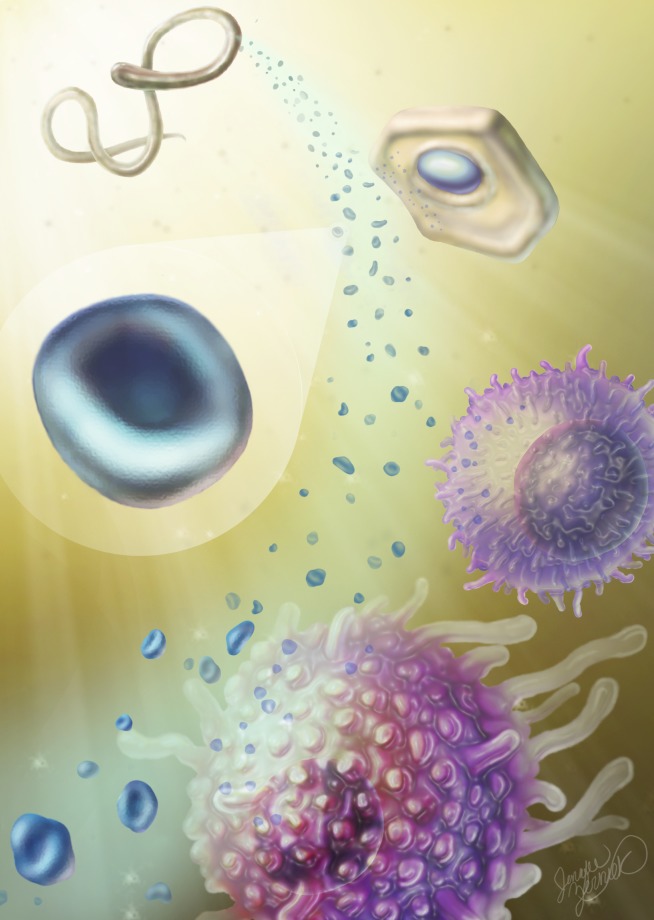
Fig 8. Filarial nematodes release EVs that are relevant at the host parasite interface.
Our model proposes that B. malayi (and D. immitis) release EV from structures including the excretory pore. These EV (magnified) are of a size and morphology consistent with exosomes but lack some canonical vertebrate exosome markers. They do, however, contain immunomodulatory effector proteins and are phagocytosed by vertebrate cells such as macrophages and potentially other relevant cell types (pictured), providing a mechanism by which these nematodes may deliver effector molecules and manipulate the host.